DTCC Case Study - Automating PCI DSS Level 1
Learn how DTCC used Cloudaware Compliance Engine to automate PCI DSS L1, hit 90% compliance, cut MTTR 49→3 days, and prevent 156 incidents.
DTCC is a leading financial services organization, managing sensitive customer payment data across multiple regions, faced growing challenges in maintaining PCI DSS Level 1 compliance across its cloud infrastructure. With over 200 AWS accounts supporting critical workloads, the organization struggled with inconsistent configurations, manual compliance checks, and delayed remediation of high-risk security issues.
Cloudaware’s Compliance Engine was selected to establish continuous compliance monitoring, automate remediation workflows, and strengthen alignment with PCI DSS requirements. By integrating AWS native security services and enforcing custom logic through Application Tags, the organization achieved a 90% compliance score, reduced mean-time-to-remediation from 49 to 3 days, and prevented 156 potential security incidents over 12 months.
Challenges
The organization’s security-first mandate highlighted several issues:
-
Inconsistent Security Configurations. AWS accounts were configured differently, leaving gaps in baseline security requirements such as encryption, IAM password policies, and logging.
-
Manual PCI DSS Monitoring. Compliance validation was performed manually, relying on ad-hoc checks and periodic audits. This created delays in identifying and addressing non-compliance.
-
Lack of Continuous Enforcement. Even when security misconfigurations were detected, there was no system in place to enforce or remediate violations in real time.
-
Limited Accountability. Without Application Tags, identifying which team owned a resource was difficult, leading to prolonged remediation cycles.
Solution
To address these gaps, the organization deployed Cloudaware’s Compliance Engine. Cloudaware’s CMDB served as the central hub for asset data, automatically discovering and consolidating information from AWS, Microsoft Azure, and third-party tools. With over 300 prebuilt rules, policy-based compliance enforcement was enabled from the start, while custom policies were created to reflect the company’s specific governance requirements. Built-in compliance dashboards provided quick visibility into industry standards with minimal setup effort.
Key elements of the solution included:
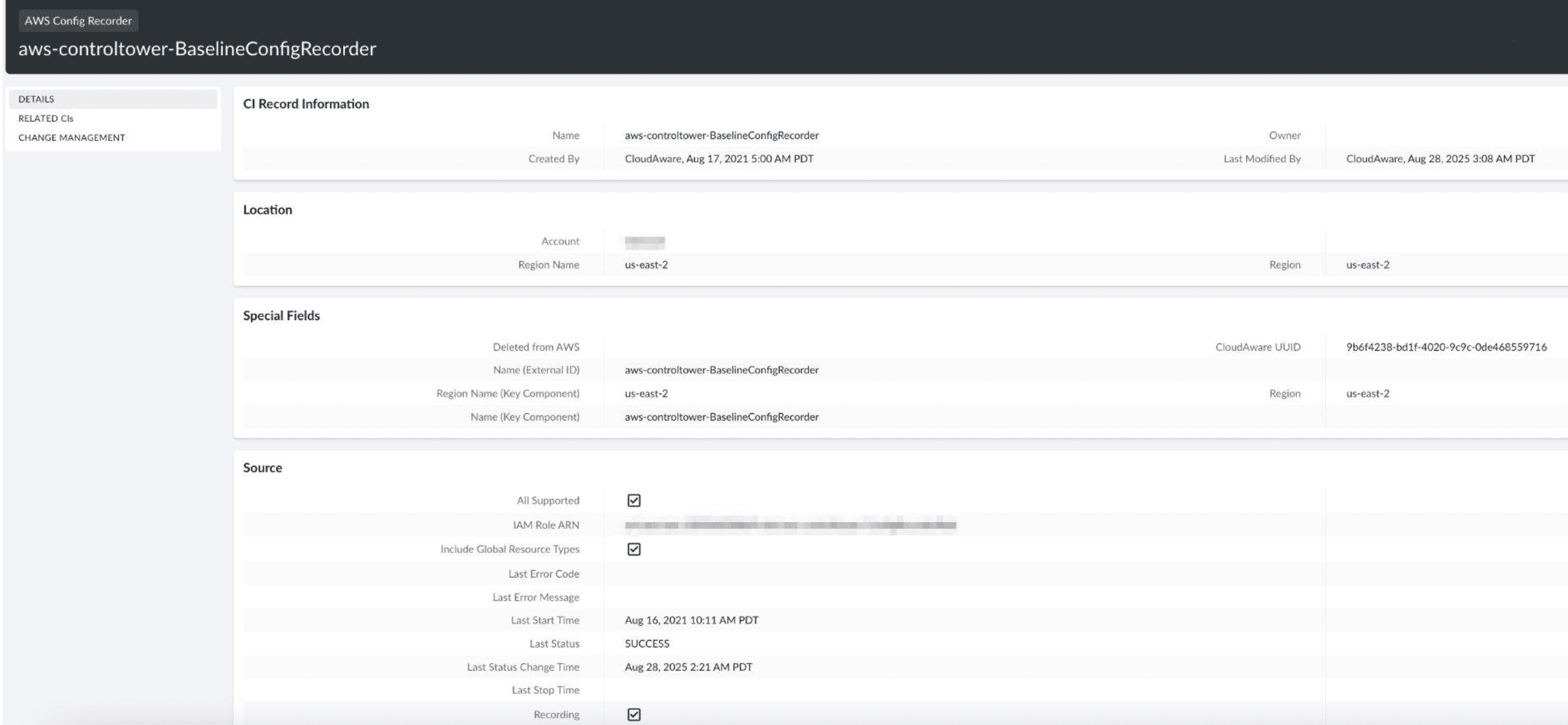
Cloudaware delivered a unified, API-driven inventory across AWS ensuring real-time visibility and data integrity. For AWS Organizations, Cloudaware first connected the management account through a CloudFormation stack, which created an IAM role with a unique External ID.
A StackSet then deployed the same IAM role across all organizational units (OUs), enabling Cloudaware to automatically discover and pull data from every member account.
Once the configuration was finalized with the role name, external ID, and management account, Cloudaware continuously synchronized account and OU data into the CMDB. Adding new accounts was straightforward, requiring only redeployment of the StackSet to the target OUs.
Integration with AWS Config enriched Compliance Engine visibility and coverage:
1. Historical Configuration Tracking
- AWS Config continuously records configuration changes to AWS resources.
- When integrated, Cloudaware’s Compliance Engine gained not just a snapshot of the current state, but also time-series data — showing when and how a resource became non-compliant.
- This helped distinguish between transient misconfigurations vs. persistent violations.
2. Completeness of Resource Coverage
- Some resources and configuration attributes were only available through AWS Config (not via direct API calls or CloudTrail).
- By ingesting Config data, Cloudaware filled gaps, ensuring broader resource visibility across all AWS services.
3. Evidence for Audits & Investigations
- Config provided a detailed audit trail of changes.
- The Compliance Engine used this trail to map violations to exact configuration drifts (e.g., when encryption was disabled, or when a security group was modified).
- This strengthened compliance evidence for PCI DSS, SOC 2, or internal audits.
4. Near Real-Time Alerts
- AWS Config triggered rules or events as soon as a configuration change occurred.
- Feeding this into Cloudaware enabled faster detection of violations, reducing Mean Time to Detection (MTTD).
5. Policy Mapping & Custom Logic
- AWS Config rules were mapped directly to Cloudaware policies, enriching context.
For example:- Config Rule: “S3 buckets must not allow public access”
- Cloudaware Policy: “S3 Bucket without block public access → Incident created”
- Together, they provided redundant coverage and validation.
6. Continuous Drift Detection
- By adding AWS Config, Cloudaware gets continuous drift detection in between scans.
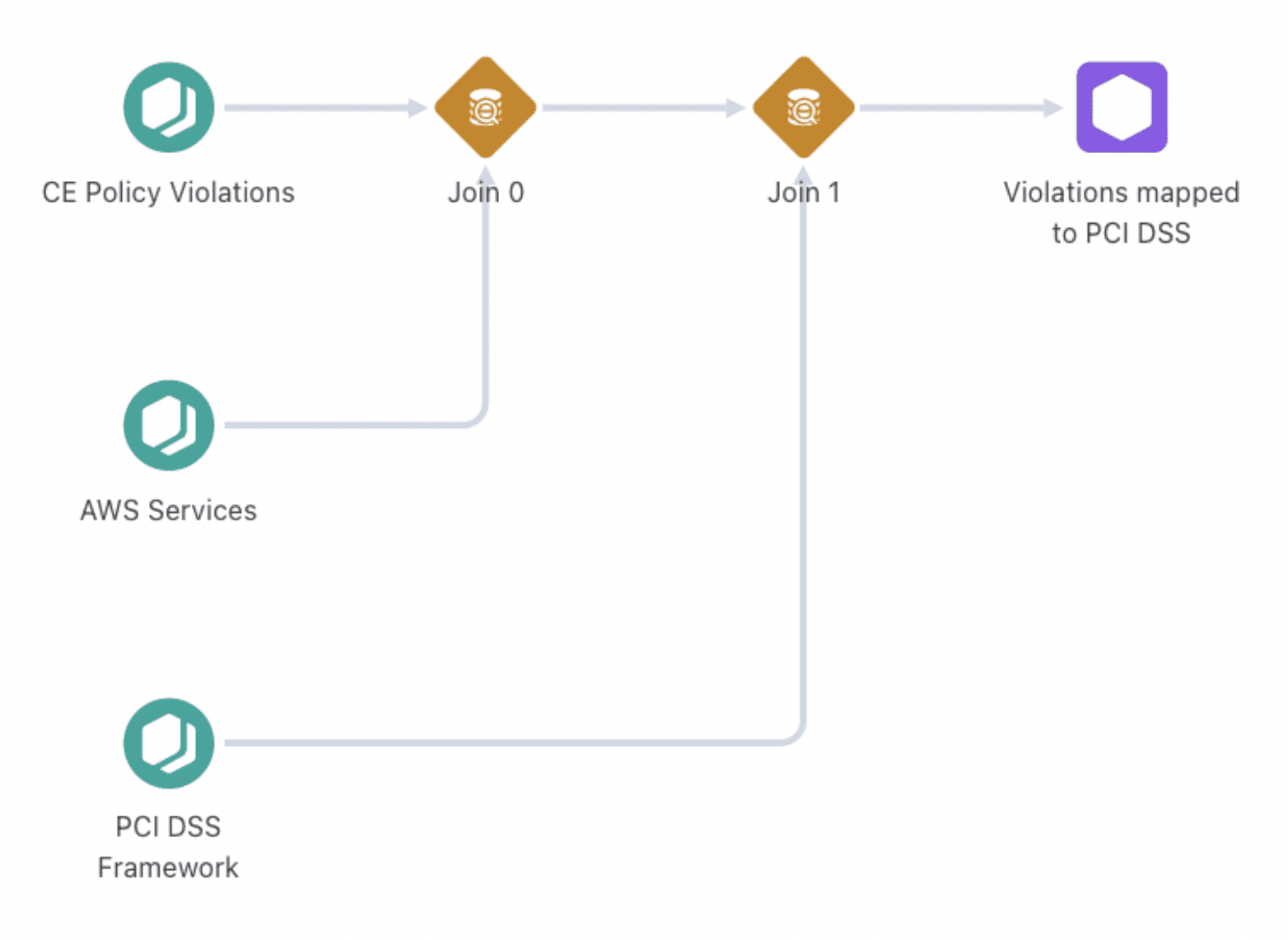
- We supported the company through the PCI DSS alignment process by leveraging Compliance Engine policies, all of which are mapped out-of-the-box to AWS Security Hub controls. These policies are also aligned with a broad range of industry frameworks, including CIS AWS Foundations, AWS FSBP, FedRAMP, NIST SP 800-53, SOC 2, and NIST CSF, ensuring that PCI DSS requirements are met within a unified compliance framework.
Policies Mapping to PCI DSS and AWS Frameworks:
| PCI DSS Requirement | Cloudaware Policies | AWS Security Hub Controls | AWS/Specific Controls |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1.1 – Establish firewall and router configuration standards | Network Security Policy | AWS EC2 Security Group allows public IPv4/IPv6 access to admin ports | [EC2.13-14] Security groups should not allow ingress from 0.0.0.0/0 or ::/0 to port 22/3389 |
| 1.2.1 – Build firewall and router configuration standards that restrict connections | Network Access Control Policy | AWS NACL allows all inbound traffic | [NACL.1] Network ACLs should restrict inbound access to necessary ports only |
| 2.2.1 – Do not use vendor-supplied defaults | IAM Policy, Account Management Policy | AWS IAM root account has MFA disabled | [IAM.1] Ensure MFA is enabled for root account |
| 3.2 – Protect stored cardholder data | Data Encryption Policy | AWS RDS instance is publicly accessible | [RDS.2] RDS DB Instances should prohibit public access |
| 3.4 – Render PAN unreadable anywhere it is stored | Data Encryption Policy | AWS S3 bucket with unencrypted objects | [S3.1] S3 buckets storing sensitive data should have encryption enabled |
| 7.1 – Restrict access based on need-to-know | Access Control Policy | AWS IAM user has excessive privileges | [IAM.3] Ensure least privilege principle for IAM users |
| 10.2 – Implement automated audit trails | Logging & Monitoring Policy | AWS CloudTrail logging is disabled | [CloudTrail.1] Enable CloudTrail logging for all regions |
| 11.2 – Run internal and external vulnerability scans | Vulnerability Management Policy | AWS Inspector findings indicate critical vulnerabilities | [Inspector.1] Schedule regular vulnerability scans using AWS Inspector |
7. Application Tag Enforcement. Cloudaware ensured every resource was tagged with the owning application. This enabled clear accountability for violations and streamlined remediation.
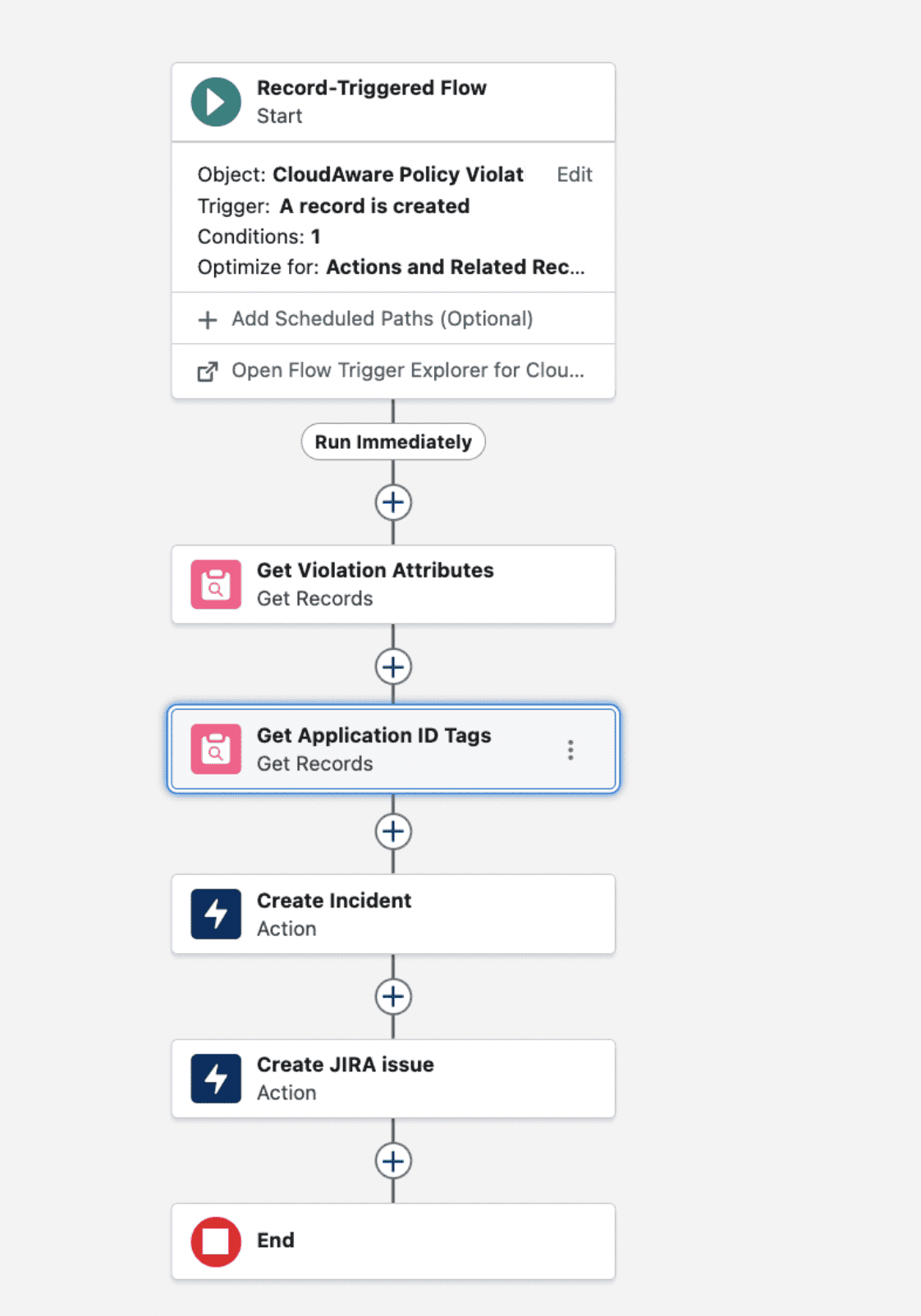
8. Incident Module Enablement. Policy violations were automatically converted into incidents, routed to responsible teams, and tracked until closure. Cloudaware was integrated with the company’s Jira instance to route compliance incidents to the appropriate teams, reducing mean time to resolution (MTTR). Additional alerts were also sent directly to individual email addresses.
Examples of incidents detected and managed through Cloudaware Compliance Engine:
- Misconfigured S3 bucket with public access → PCI DSS 3.4 violation.
- Disabled CloudTrail logging → PCI DSS 10.2 violation.
- IAM user with excessive privileges → PCI DSS 7.1 violation.
Incident Response Workflow:
- Detection – AWS Config/Cloudaware Compliance Engine identifies a violation and maps to the corresponding security control..
- Incident Creation – Cloudaware Incident Module automatically generates an incident.
- Assignment – Incident routed to the owning team based on Application Tags.
- Remediation – Team performs manual or automated remediation.
- Closure – Incident closed with supporting audit evidence.
Incident Categorization:
| Severity | Description / Example |
|---|---|
| Critical | Direct PCI DSS violation with high data exposure risk (e.g., unencrypted payment data). |
| High | Major misconfiguration affecting compliance but limited exposure (e.g., CloudTrail disabled). |
| Medium | Security control gap with compensating controls in place (e.g., IAM over-permissioning). |
| Low | Minor configuration drift, low risk to cardholder data (e.g., tagging misalignment). |
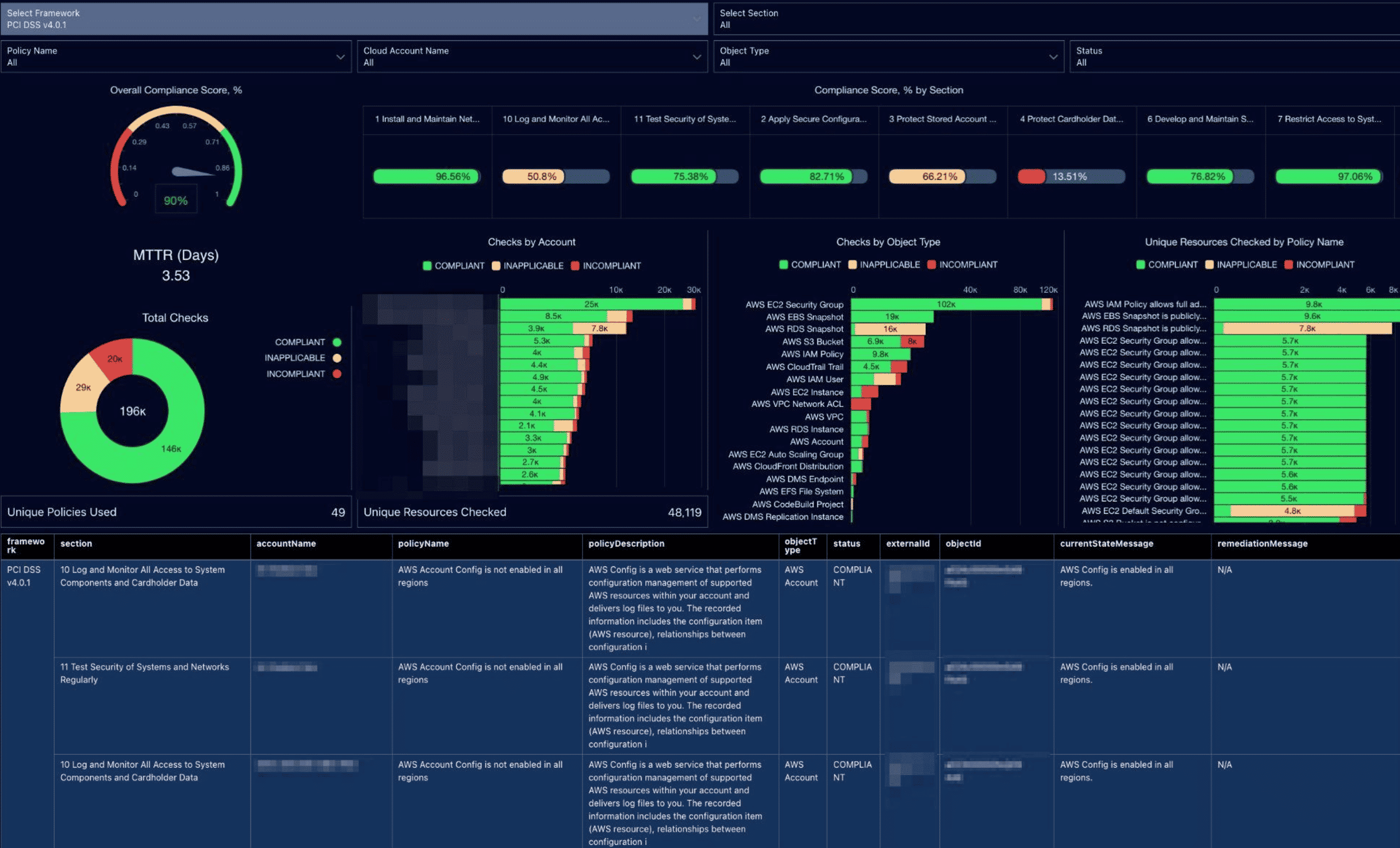
Using Analytics Studio, the company leveraged BI to prioritize remediation efforts on the most impactful compliance engine policies. Executives monitor compliance engine dashboards to track violation trends and mean time to resolution (MTTR), enabling data-driven decision-making.
For each non-compliant resource, Compliance Engine policies offered step-by-step remediation guidance to facilitate resolution, with built-in documentation and reference materials included for support
Together, these components created a continuous compliance ecosystem with automated monitoring, actionable insights, and remediation workflows.
Compliance Requirements & Policy Coverage
The Compliance Engine enforced policies aligned with PCI DSS Level 1 controls. Examples include:
| PCI DSS Requirement | Cloudaware Policy | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 8.3.1 Multi-factor Authentication | IAM User MFA Not Enabled | Ensures MFA is enabled for all IAM users with console passwords |
| 3.4 Protection of Cardholder Data | EBS Volume Encryption Not Enabled | Enforces encryption at rest for EBS volumes |
| 10.2 Logging of User Activities | CloudTrail Not Enabled in All Regions | Ensures logging and monitoring of all activities |
| 1.1 Network Security Controls | Security Group Allows Public Admin Ports | Identifies unrestricted SSH/RDP access |
| 10.3 Audit Trail Integrity | CloudTrail Log File Validation Disabled | Ensures logs are tamper-proof |
| 6.5 Secure Development | CodeBuild Source with Credentials | Prevents exposure of credentials in build projects |
All policies contained custom logic provided by the organization to reflect specific operational and compliance needs.
Privacy Controls
To strengthen privacy controls and PCI DSS alignment, the following measures are implemented:
- PCI DSS Data Protection (Req. 3.2, 3.3, 3.4):
Compliance Engine continuously validates that cardholder data (e.g., PAN) is stored only in approved, encrypted repositories. It detects attempts to disable encryption on S3 buckets, RDS instances, and EBS volumes, automatically generating incidents for remediation. - Encryption (Req. 3.5, 4.1):
- Data at rest: AES-256 encryption is enforced across all storage layers (S3, EBS, RDS).
- Data in transit: All communication must use TLS 1.2 or higher. Any resources configured with weak ciphers or insecure protocols are flagged as non-compliant.
- PAN masking and truncation policies are enforced where applicable, ensuring unreadable storage of cardholder data.
Key Management (Req. 3.6, 3.6.4, 3.6.6):
- AWS KMS is integrated with Hardware Security Modules (HSMs) meeting FIPS 140-2 standards.
- Key lifecycle management includes secure generation, storage, distribution, and deactivation.
- Compliance Engine verifies that key rotation policies are active and that decommissioned keys are retired securely.
Data Handling Procedures (Req. 7.1, 7.2, 8.7):
- Application Tags classify data sensitivity, ensuring PCI-related resources are segregated.
- Policies enforce that tagged PCI resources cannot be deployed without encryption and logging enabled.
- Data retention policies are validated to ensure sensitive data is only stored for the minimum required duration.
Access Controls (Req. 7, 8, 10):
- IAM roles and policies enforce least privilege access to cardholder data.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is mandatory for all privileged and console users.
- CloudTrail ensures that every access event is logged, with log file validation preventing tampering.
- Compliance Engine maps CloudTrail data to PCI DSS 10.x requirements, ensuring automated audit trails are maintained and reviewed.
Technical Implementation
The rollout of the compliance program was executed using a structured, phased approach to ensure comprehensive coverage, minimal disruption, and actionable insights:
- Discovery Phase. All existing AWS accounts, resources, and configurations were inventoried and ingested into the Cloudaware Configuration Management Database (CMDB). This phase established a complete, centralized view of the cloud environment, enabling accurate mapping of resources to PCI DSS requirements and identifying initial gaps in compliance.
- Policy Deployment. PCI DSS compliance policies were configured within Cloudaware and rigorously tested against baseline environments to validate accuracy and effectiveness. Each policy included automated checks, remediation guidance, and reference documentation, ensuring that both technical teams and auditors could clearly understand compliance requirements.
- Integration. Key AWS security and governance services—including AWS Config, Security Hub, CloudTrail, and GuardDuty—were integrated with Cloudaware. This integration enabled the real-time collection of configuration data, security findings, and audit logs, creating a unified view of compliance posture across the organization.
- Application Tagging Enforcement. A tagging enforcement mechanism was implemented to ensure that all cloud resources included the required metadata for ownership, environment, and sensitivity classification. Non-compliant resources were automatically flagged and tracked until proper tagging was applied, enhancing governance and simplifying compliance reporting.
- Incident Automation. Policy violations detected by Cloudaware were automatically converted into actionable incidents and routed to the appropriate owning teams via Jira. This automation reduced manual intervention, improved response times, and provided clear ownership for each compliance issue, contributing to a lower mean time to resolution (MTTR).
- Continuous Monitoring. Compliance scans were scheduled to run daily, with near-real-time alerts generated for critical or high-priority violations. Executives and security teams monitored compliance dashboards to track violation trends, remediation progress, and MTTR, enabling proactive risk management and informed decision-making.
Architecture Overview
The architecture diagram below provides a detailed view of the security architecture. It shows AWS service interaction flows, security control implementation points, and monitoring points.
Key Flows:
- AWS Config, Security Hub, Inspector, GuardDuty continuously feed compliance and security data.
- Cloudaware Compliance Engine evaluates this data against PCI DSS policies.
- Violations are converted into incidents and routed to responsible teams via Jira and email.
- Dashboards provide executives and auditors with continuous compliance reporting.
Compliance Engine Reference Architecture
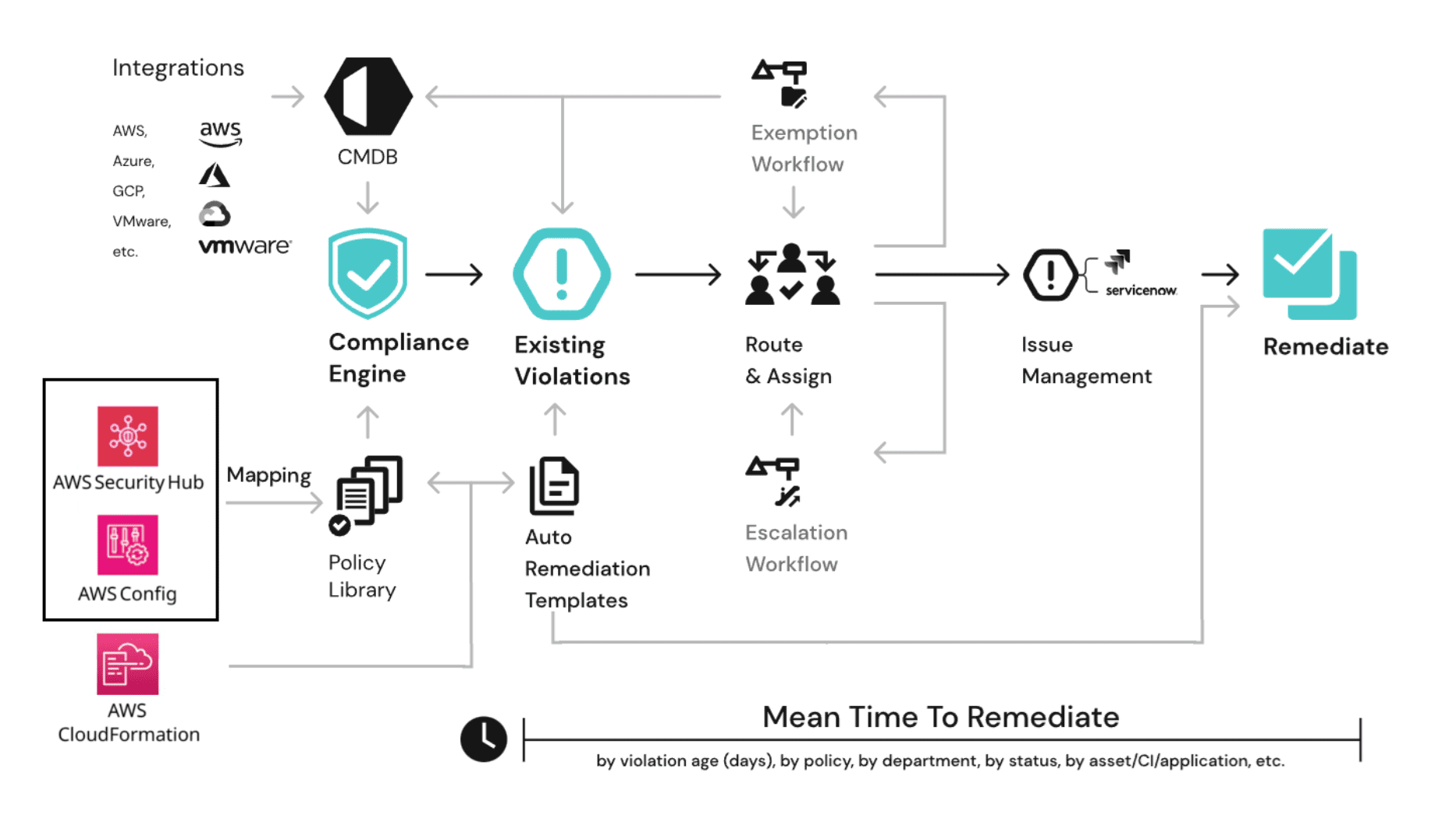
AWS resources monitored via AWS Config
Security findings generated by Cloudaware Compliance Engine

Compliance Engine evaluates resources against PCI DSS policies.
Violations → Incidents created in Cloudaware Incident Module.
Teams notified with ownership based on Application Tags.
Continuous reporting via Compliance and Security Dashboards.
Security Outcomes & Metrics
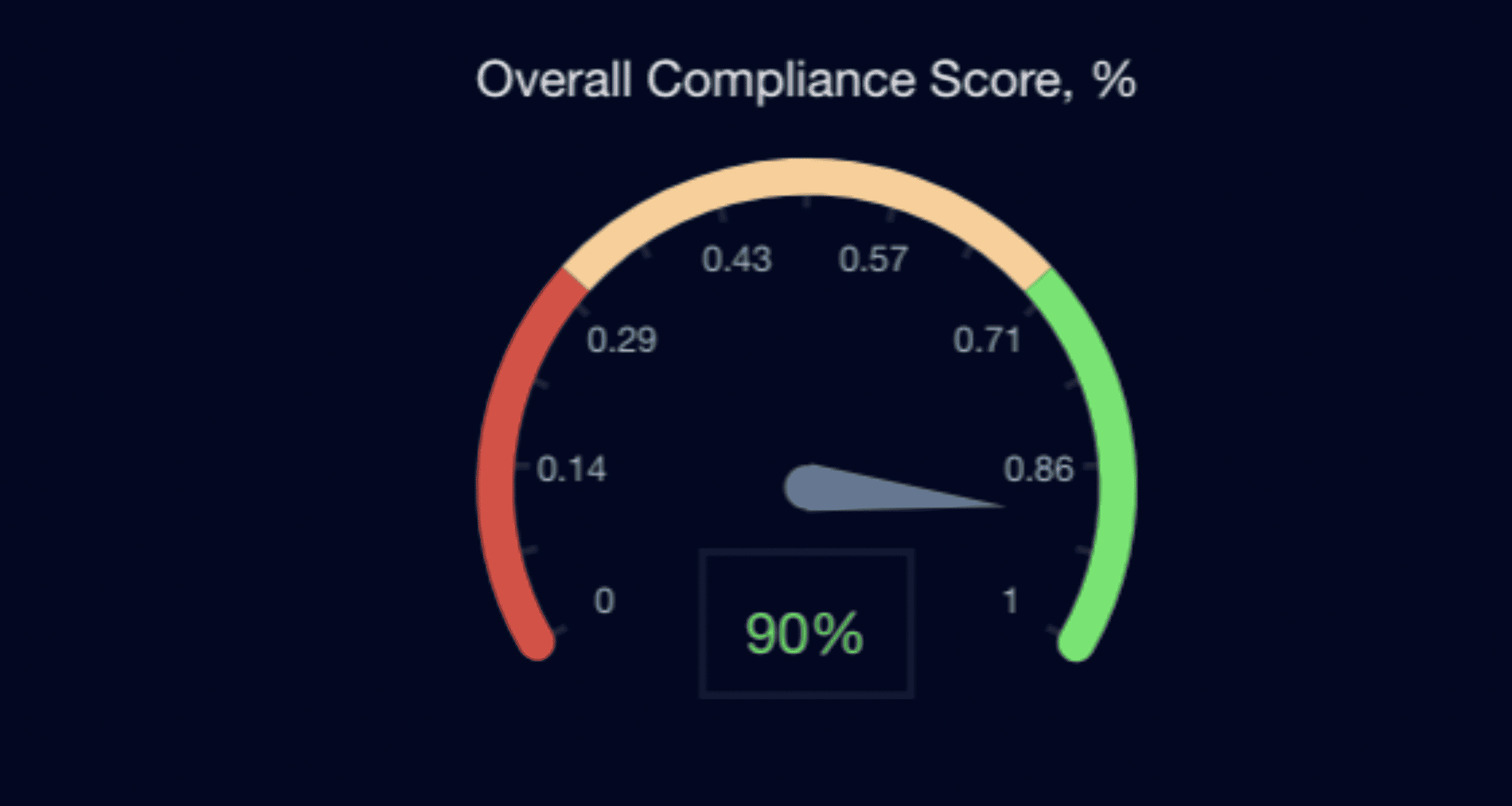
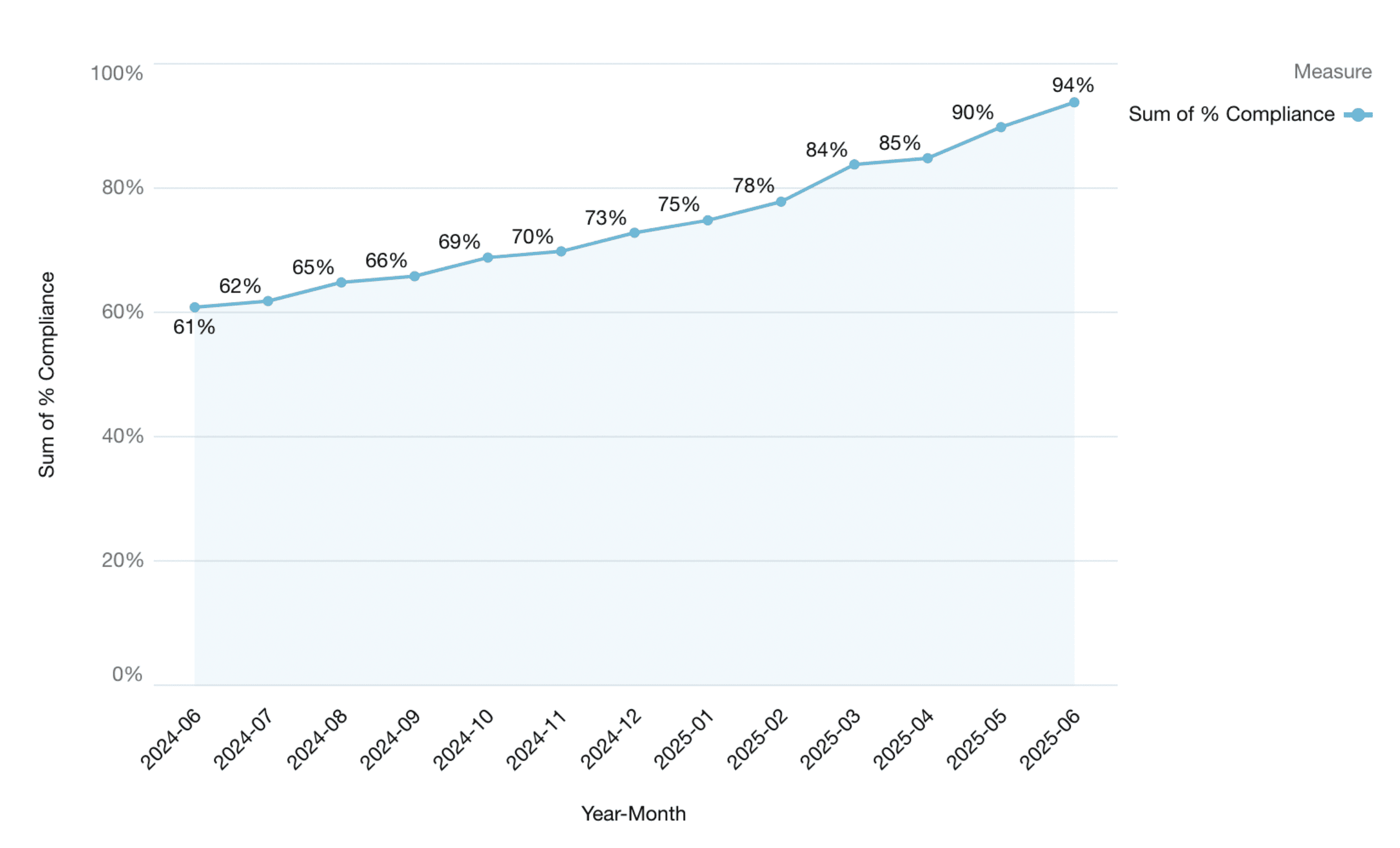
The financial organization achieved measurable improvements:
Before Implementation:
- Manual compliance monitoring
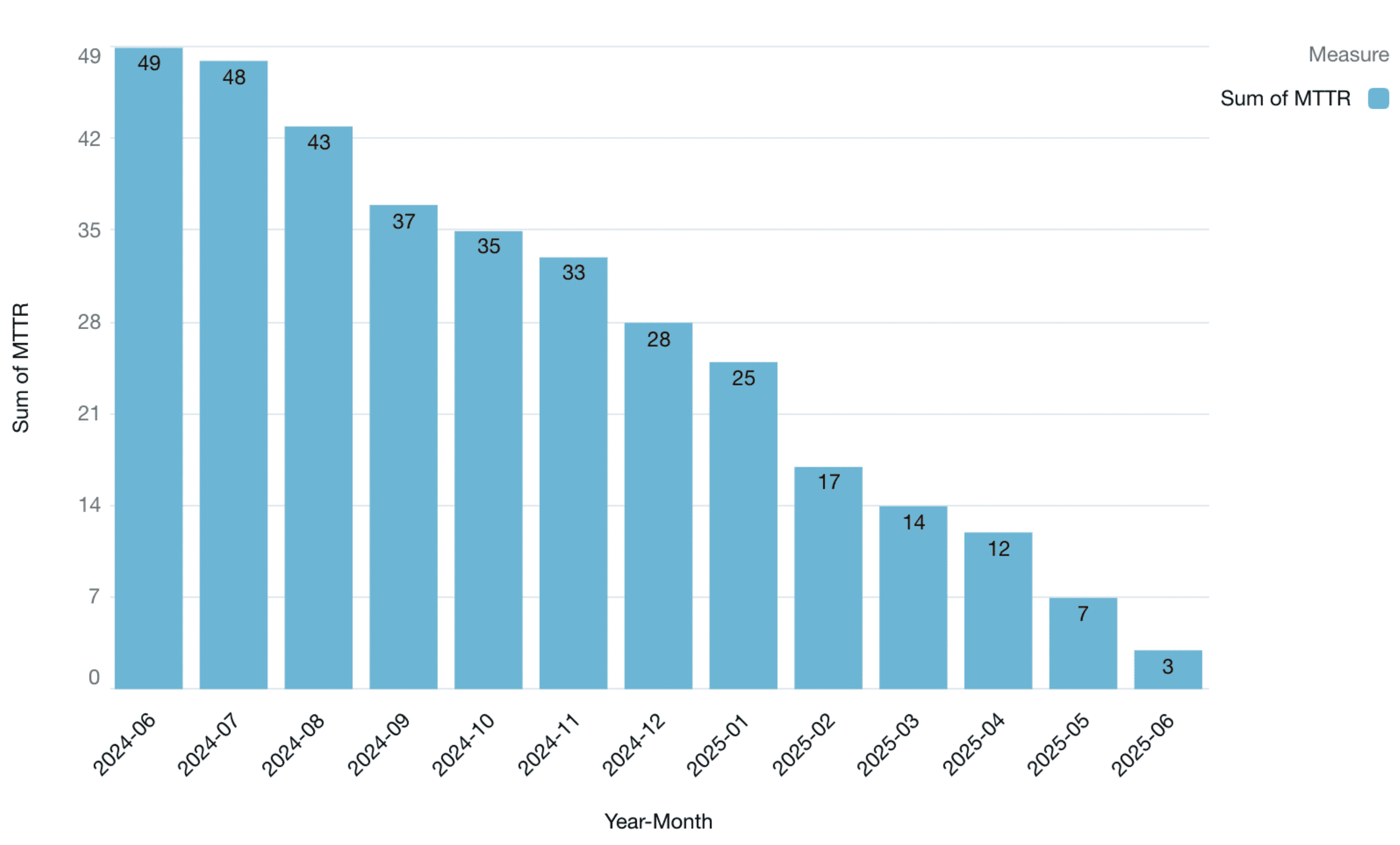
- 48 days average MTTR
- 61% compliance score
After Implementation:
- Automated, continuous monitoring
- 3.53 Days MTTR for critical findings
- 95% compliance score (avg. 90% maintained)
- 89% reduction in critical findings
- 156 incidents prevented within 12 months
Compliance Score Trend (Before vs After)
MTTR Score Trend (Before vs After)
Customer Validation
"Cloudaware's Security Compliance Engine transformed our security posture from reactive to proactive. We now maintain 90% compliance and reduced incident response time by 85%."
— Chief Information Security Officer, Financial Organization
Conclusion
By adopting Cloudaware’s Compliance Engine, the financial organization established a robust, automated compliance framework mapped directly to PCI DSS Level 1. With Application Tag enforcement, integrated AWS security services, and automated incident workflows, the organization reduced risks, improved audit readiness, and achieved sustainable compliance.
Key Benefits:
- Continuous PCI DSS monitoring
- Reduced risk exposure and audit costs
- Faster remediation with clear accountability
- Security-first culture embedded across cloud operations
Ready to control your multi-cloud budget like Boeing?
Schedule a Cloudaware FinOps demo to discover potential savings in your AWS, Azure, or GCP environments.
