If you’ve ever had to track down a forgotten EC2 instance racking up charges or explain why there are orphaned VMs in every region, you know the struggle of IT asset audits. It’s not just about ticking compliance boxes — it’s about regaining control over sprawling multi-cloud and on-prem environments before they turn into an operational nightmare.
Having done this more times than I can count, I can tell you that a proper IT asset audit isn’t about manually chasing down rogue instances, unused licenses, or forgotten Kubernetes clusters. It’s about having a structured process and the right tool to do it efficiently. That’s where a solid IT asset management checklist comes in.
In this guide, I’ll walk you through a 9-step audit framework — all streamlined into a single tool: Cloudaware. No spreadsheets, no manual guesswork — just complete visibility across your infrastructure.
Let’s get started 👇
1. Define Audit Scope & Objectives before your audit
Before you even think about running an asset audit, take a step back. Otherwise, you’re just opening Pandora’s box of misconfigured instances, shadow IT, and assets that nobody remembers deploying.
The key here? Set clear boundaries and objectives, so your audit doesn’t spiral into an endless hunt for every stray YAML file in existence.
1. What Are You Auditing?
Are you focusing on compute instances (EC2, GCE, Azure VMs, on-prem servers)? Or is this about network assets (load balancers, firewalls, VPC peering configs)? Maybe you need to tackle SaaS license sprawl because someone decided the company needed both Jira and Asana.
The more specific your scope, the faster and cleaner your asset audit will be.
📌 Pro move: If your infra spans multiple clouds and on-prem, map out which environments you're covering. Are you auditing production, staging, and test environments, or just the main pipeline? You don’t want to waste time tracking down dev sandboxes that exist solely for chaos engineering experiments.
2. What’s the Business Goal?
IT audits aren’t just for the thrill of the hunt (tempting, I know).
Are you cutting costs?
Tightening security posture?
Cleaning up for an upcoming compliance audit (ISO 27001, SOC 2, CIS benchmarks)?
Each goal shifts how you approach the audit.
💡 Example: If cost savings is the focus, your asset management audit will zero in on orphaned EBS volumes, unused reserved instances, and forgotten Kubernetes worker nodes. If security is the concern, expect a deep dive into IAM policies, open security groups, and compliance drift in CIS-hardened images.
3. Who’s involved?
You don’t audit in a vacuum. Decide upfront which teams need to be looped in.
- Cloud architects & DevOps → They know where the bodies are buried.
- Security teams → If you’re touching IAM, RBAC, or network policies, they must be involved.
- Finance/FinOps → If this is about cloud costs, they’ll want reports that make sense in actual dollars, not CPU cycles.
4. Tooling: One Audit, One Platform
If your plan includes manually sifting through AWS Cost Explorer, Azure Advisor, GCP logs, and on-prem monitoring tools, congratulations — you’ve just signed up for weeks of pain. Instead, centralize the process.
👉 Cloudaware’s asset management software lets you run a full asset audit across AWS, Azure, GCP, and on-prem in one place. That means no jumping between dashboards or manually correlating data across multiple platforms. Just one pane of glass, all assets, 10 steps, done.
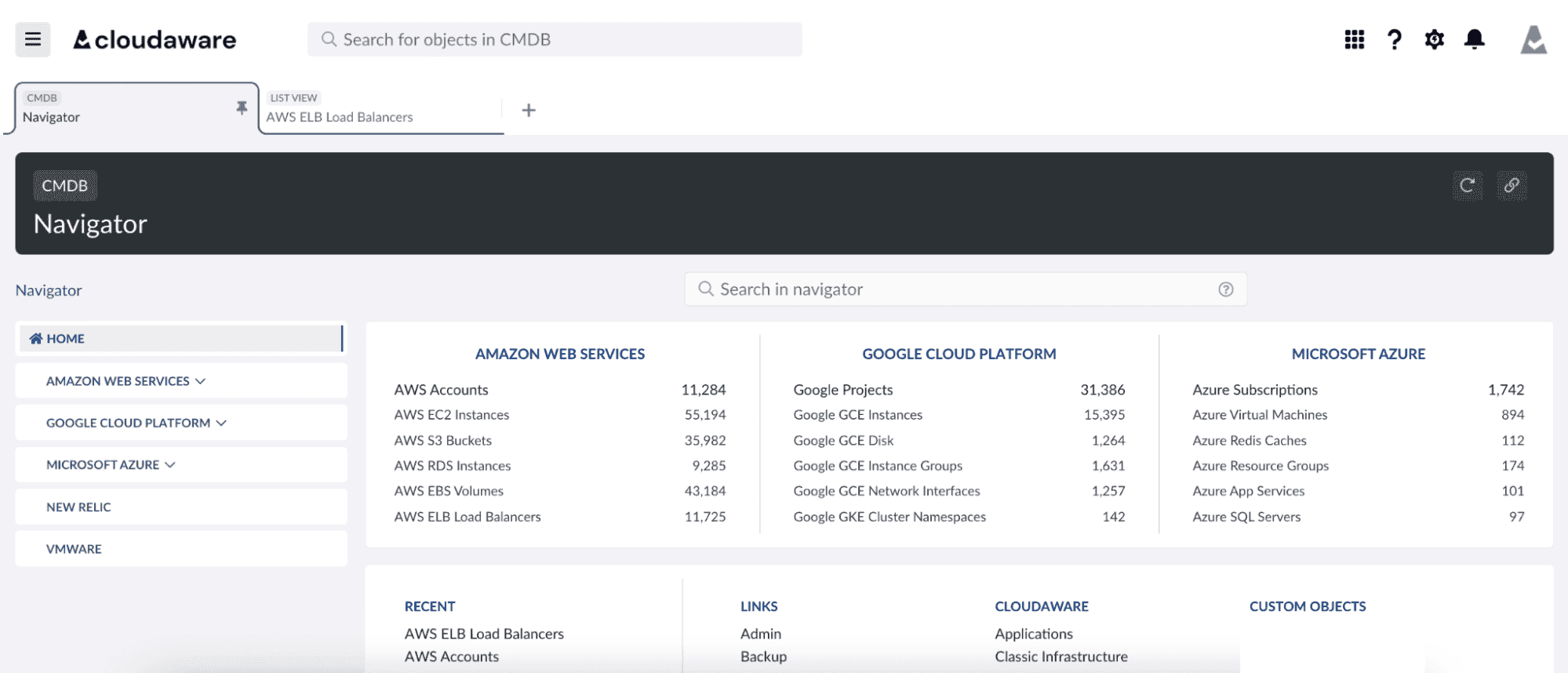
Define exactly what assets you’re auditing, why, who’s involved, and what tools you’re using. Otherwise, you’ll end up drowning in cloud sprawl instead of fixing it.
Once you’ve got this locked in, Step 2 is where the real work begins.
2. IT Assets Discovery & Inventory Collection
Alright, so you’ve mapped out the scope of your IT asset audit — now it’s time to roll up your sleeves and get into discovery & inventory collection. This step is where things get real because what you don’t find will come back to haunt you.
Start by sweeping everything: cloud, on-prem, edge, shadow IT — if it exists, it’s yours to track.
- Compute: VMs, containers, bare metal, serverless functions (Lambda, Azure Functions).
- Storage: Block, object, file storage — EBS volumes, S3 buckets, NAS, SANs.
- Networking: VPCs, subnets, security groups, load balancers, VPNs, direct connects.
- Software & Configs: OS versions, installed packages, security patches, middleware (think databases, app servers, messaging queues).
- IAM & Permissions: Who can do what? Admin accounts, service accounts, API keys floating around untracked.
Surely no one wants to spend their days chasing down mystery assets or hunting for rogue VMs hiding in some forgotten corner of your inventory. That’s where Cloudaware CMDB steps in and saves you from the chaos.
It hooks into AWS, Azure, GCP, and your on-prem setup all at once, pulling in everything — no blind spots, no “I swear this VM didn’t exist yesterday” moments.
And the best part? It’s real-time and agentless. No tedious installs, no “deploy this script across a thousand servers” headaches — just instant, automatic asset discovery and inventory collection.
It talks to cloud APIs, hypervisors, and network layers constantly, keeping your data fresh and ensuring your IT asset audit is always on point. That means no stale records, no missing assets, no wondering if that S3 bucket is still floating around untagged, waiting to cause you problems.
Book a demo to know how Cloudaware can help your infrastructure visibility
3. Implement & Verify Tagging Standards
Tagging isn’t just about keeping things organized — it’s critical for cost tracking, security, and compliance in your IT asset management audit program. A well-structured tagging policy ensures that every asset in your inventory is properly classified, making audits seamless.
But here’s the challenge: if your tags are inconsistent, missing, or outdated, your reports become unreliable.
How to Implement Tagging Standards in Cloudaware
1️⃣ Define a Standardized Tagging Schema. Ensure every asset follows a structured format with tags like:
- Environment (Production, Staging, Dev)
- Owner (Team or Individual Responsible)
- CostCenter (Billing & Chargebacks)
- Compliance (PCI, HIPAA, SOC2)
2️⃣ Automate Tag Enforcement. Use Cloudaware’s policy engine to detect and remediate untagged or incorrectly tagged assets in real time.
3️⃣ Integrate with Cloudaware CMDB. Cloudaware ingests and normalizes tagging data from AWS, Azure, GCP, and on-prem, ensuring asset management software solutions maintain cross-cloud consistency.
Verifying Tagging Compliance with Cloudaware
With Cloudaware’s Tag Analyzer you can instantly identify tags coverage across your entire environment, untagged assets, inconsistent tag formats, outdated or incorrect values.
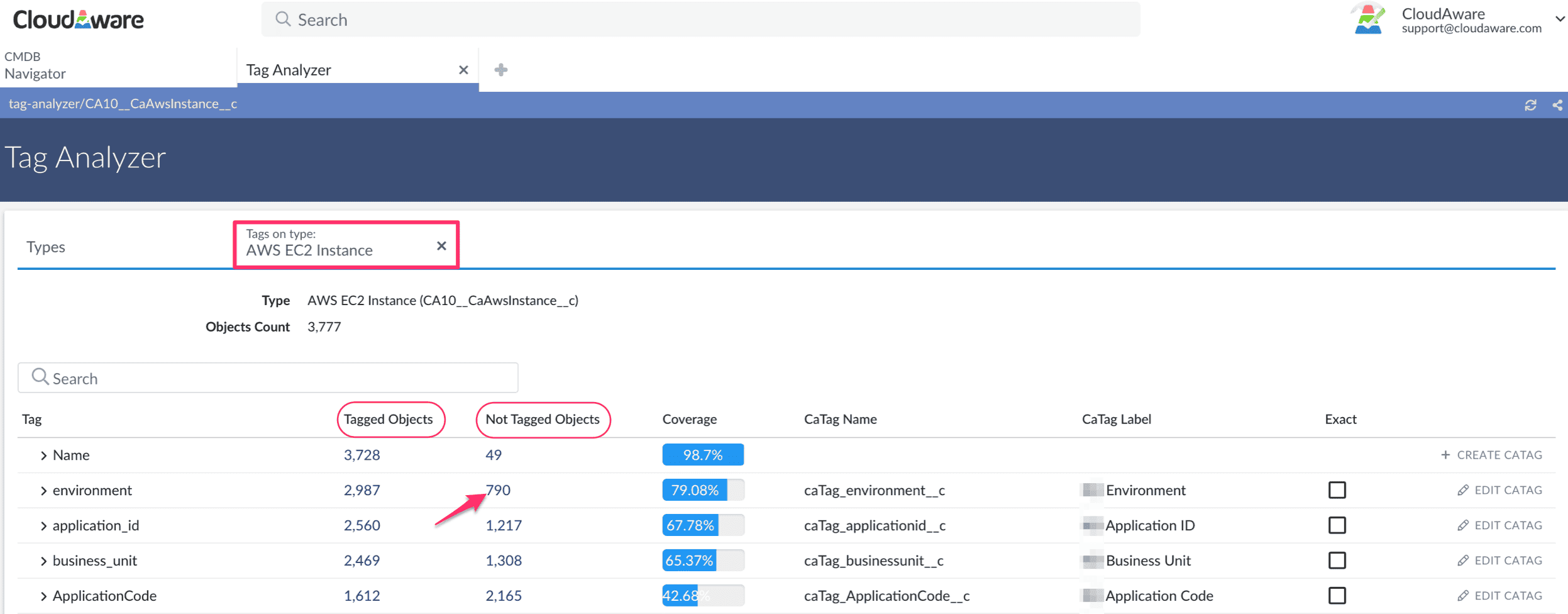
Example: A Cloudaware client running an IT asset audit discovers that 15% of their cloud assets lack cost allocation tags — leading to budget overruns. With Cloudaware’s automated tagging enforcement, they fix compliance gaps instantly.
If you don’t enforce tagging, you’re flying blind. Standardize, audit, and automate with Cloudaware’s asset management solutions — or expect chaos.
Read also: Top 10 benefits of IT asset management in 2025
4. Evaluate Asset Conditions
Alright, now that we’ve discovered everything and tagged it properly, it’s time for a status check — because not all assets age gracefully. Some are sitting there burning money, others are dragging performance down, and a few might just be waiting to fail spectacularly.
This step in the IT asset audit ensures that every resource is optimized, functional, and cost-effective.
✅ Monitor Performance & Usage Trends of the Cloud Assets
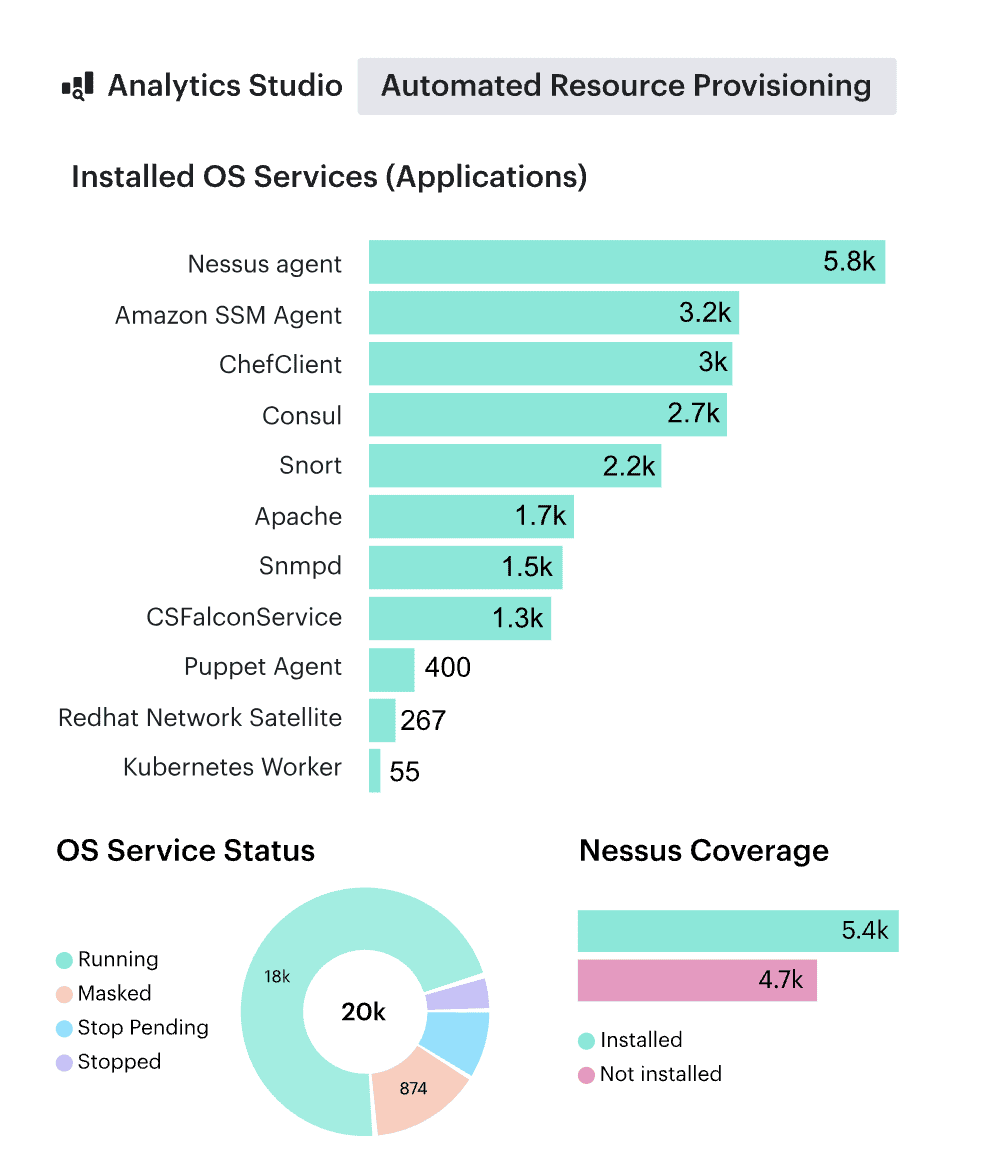
- Not every asset is pulling its weight. Check CPU, memory, and disk utilization — if something is consistently underused, it’s time to resize or retire.
- Scan for zombie resources — EBS volumes nobody detached, IPs that lost their purpose, and snapshots hoarding storage space.
- Identify missing or inconsistent tags — because misclassified assets can throw off cost tracking and make asset management a mess.
✅ Assess Hardware & OS-Level Health of the On-Premises Assets
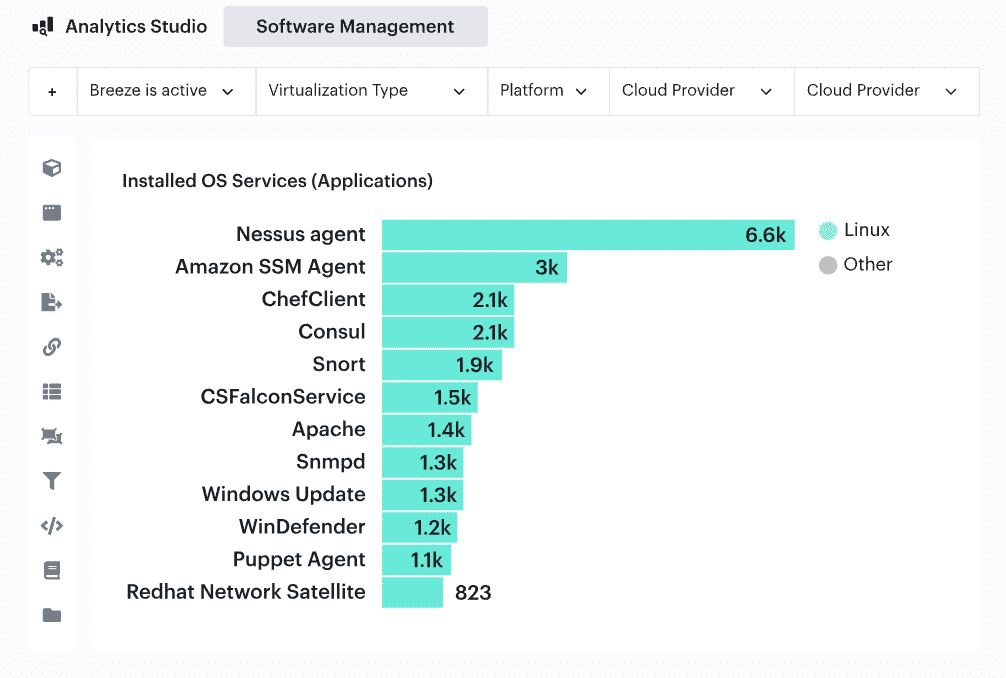
- Track server configurations, system logs, and OS versions — because an unpatched system is just waiting to break at the worst moment.
- Identify aging servers before they become unexpected downtime stories. If something’s running on warranty fumes, plan the replacement, not the disaster recovery.
- Keep an eye on mount points, installed software, and services — because a critical process crashing unnoticed can turn into an emergency way too fast.
5. Correlate related CIs to understand interdependencies
Alright, picture this: your team gets a high-priority alert — an application is down. You check the logs, restart the service, even scale up resources. Still broken. Meanwhile, users are piling into the incident chat, and someone is already suggesting rolling back last night’s deployment.
But here’s the real kicker — the issue isn’t even in the app. It’s an expired IAM role on an EC2 instance that lost access to its RDS database. No one saw it coming because no one mapped the dependencies.
How to Prevent This Chaos
✅ Map Every Connection That Matters
- Your compute instances aren’t just servers. They have attached storage, security groups, and IAM roles that control access.
- Your databases don’t exist in a vacuum. They rely on private networking, peering connections, maybe even external identity providers.
- Your applications span across cloud and on-prem, juggling API calls, load balancers, Kubernetes clusters, and backend services.
- Take an EC2 instance. In Cloudaware, you instantly see:
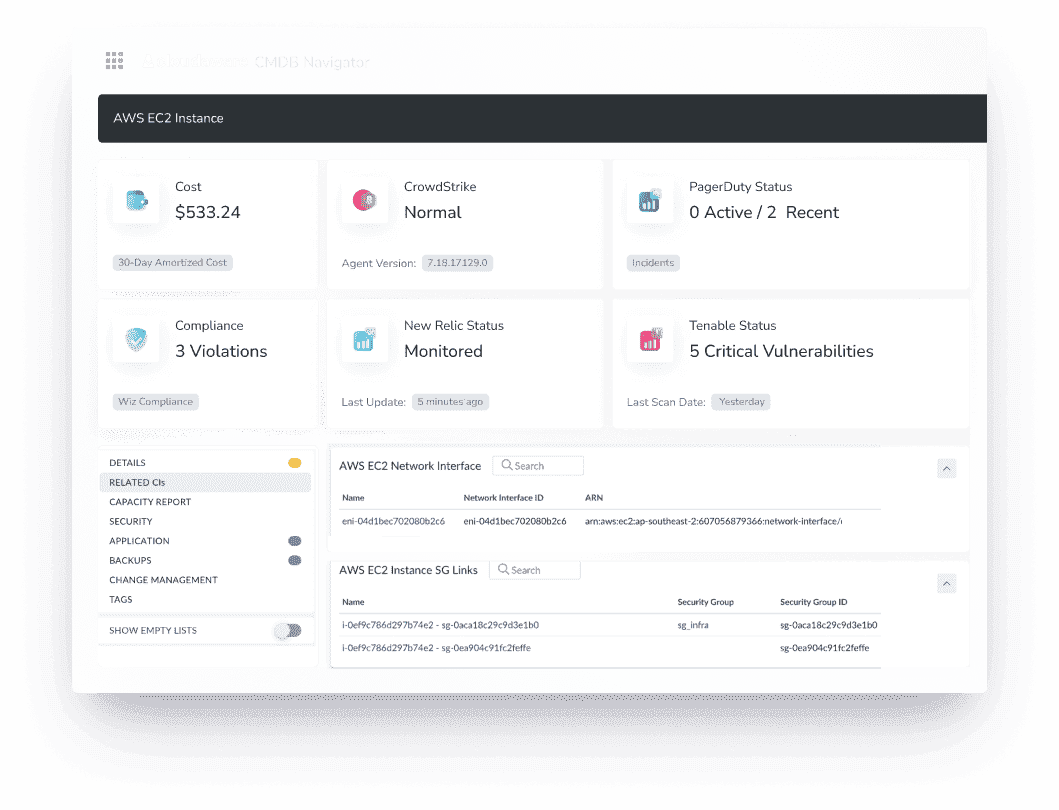
- What it’s connected to — databases, storage, subnets, IAM roles
- What security groups it’s using — open ports, misconfigurations
- What applications or workloads are running on it
Now, when it’s audit time, you’re not scrambling — you’re pinpointing. No more guessing, no more wasted time, just clear insights into your IT asset audit inventory.
This step in the audit asset management process ensures assets are properly linked, reducing blind spots and making asset management software solutions actually useful.
6. Gather Security & Vulnerability Insights
You know the drill — security isn’t a box you check, it’s a constant battle. At this step of the IT asset audit, you’re not just looking for misconfigurations — you’re hunting for risks before they turn into breaches.
Because in a hybrid, multi-cloud setup, all it takes is one forgotten S3 bucket, an unpatched EC2 instance, or an exposed database to put your company at risk.
Where to Focus Your Security & Vulnerability Checks
✅ Cloud Asset Exposure
- Scan for publicly accessible S3 buckets, open RDP/SSH ports, and misconfigured security groups.
- Check IAM policies — who has access to what? Overly permissive roles (e.g., AdministratorAccess granted to a service account) can be an open invitation for trouble.
- Monitor API keys and credentials — are they encrypted? Rotated? Or worse, leaked somewhere in a repo?
✅ On-Prem & OS-Level Vulnerabilities
- Identify unpatched servers — outdated kernel versions, old software packages, or missing security updates create easy attack vectors.
- Track EOL (end-of-life) systems — that old Ubuntu 16.04 server running a critical app? It’s not just legacy, it’s a liability.
- Ensure proper tracking of unauthorized processes or unexpected services — because if something new is running, you better know why.
Take an EC2 instance, for example. In Cloudaware, you can instantly see:
- Open ports, security group rules, and risky configurations
- OS vulnerabilities based on CVE databases
- Patch status and outdated software
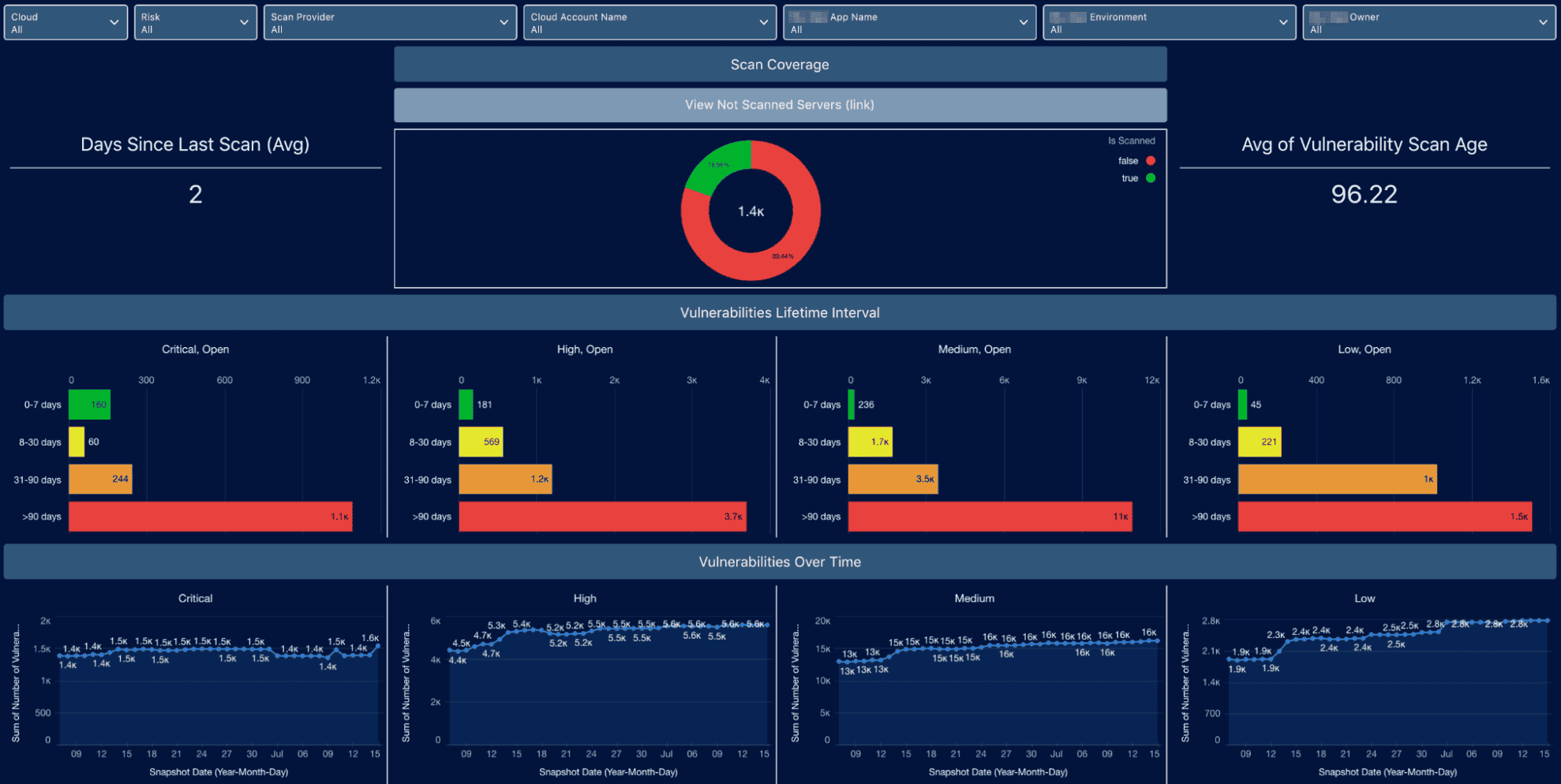
The vulnerability report in Cloudaware.
A proper audit of IT asset management isn’t just about listing assets in an inventory — it’s about ensuring they’re secure, patched, and hardened. This process demands the right tools, software, and solutions to keep your business equipment protected in real time. Audit, fix, repeat.
7. Track Asset Lifecycle
Assets don’t last forever, and in a hybrid multi-cloud setup, keeping track of what’s active, outdated, or decommissioned is critical. At this step of the IT asset audit, the goal is to ensure every server, VM, database, and network component is properly tracked, managed, and optimized.
Without a clear asset management strategy, business costs spiral, security risks increase, and outdated equipment lingers longer than it should.
Where to Focus Your Lifecycle Tracking
Provisioning & Deployment
👉 Track when and how an asset was created — whether it's an EC2 instance, Azure VM, or an on-prem host.
👉 Ensure proper tagging and metadata assignment — missing data makes later tracking and audits a nightmare.
Active Usage & Optimization
👉 Monitor real-time asset status and resource usage trends — is it still active, underutilized, or orphaned?
👉 Identify stale assets, like unattached EBS volumes, forgotten snapshots, or abandoned VMs, to optimize resources and reduce unnecessary costs.
👉 Ensure firmware, OS, and software updates are happening on schedule to prevent security risks.
End-of-Life & Decommissioning
👉 Detect aging infrastructure and outdated software versions to plan upgrades before failures occur.
👉 Ensure proper decommissioning workflows, such as removing assets from CMDB, unassigning IPs, and securely retiring hardware.
Without proper tracking in an IT asset management process, expect surprise costs, compliance issues, and operational headaches.
8. Compliance Tracking & Policy Enforcement
You know how it goes — compliance isn’t a one-and-done task. It’s a constant chase, where one missed setting can turn into an urgent fix when the audit team shows up.
In a hybrid multi-cloud setup, where assets spin up and down across AWS, Azure, GCP, and on-prem, keeping everything in check takes more than good intentions. It takes continuous enforcement and strong auditing asset management practices.
Where to Focus Your Compliance Tracking
✅ Cloud Security & Access Policies
- Who has access to what? Scan IAM roles, security groups, and firewall rules to catch overly permissive access, like an EC2 instance open to the world.
- Ensure encryption is enforced — no excuses for unencrypted S3 buckets or databases with sensitive data.
✅ Software & Configuration Compliance
- Patch levels matter. An unpatched system isn’t just a security risk — it’s a compliance failure waiting to be flagged.
- EOL systems are liabilities. If an old RHEL 6 server is still running a critical app, it needs a plan — now, not when it’s already failed.
✅ Audit-Ready Policy Enforcement
- Prevent configuration drift. If someone overrides a security setting, catch it before it becomes the new normal.
- Verify logging and backup policies. If logs are missing or backups aren’t following retention policies, that’s a major problem.
For an EC2 instance, Cloudaware automatically flags misconfigurations, like an unpatched OS, missing encryption, or an exposed port. 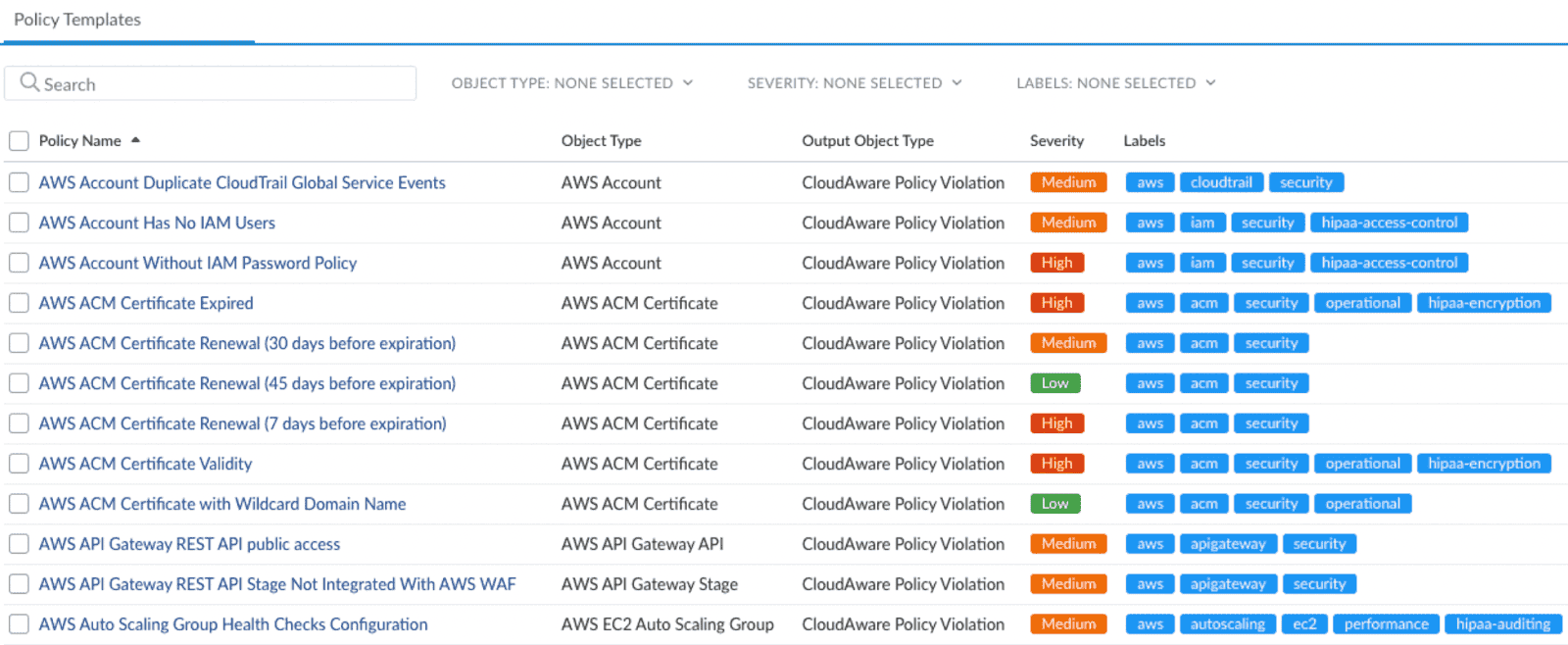 So you can be sure compliance gaps are caught before they become audit failures.
So you can be sure compliance gaps are caught before they become audit failures.
9. Apply Depreciation & Cost Tracking
In a hybrid multi-cloud setup, assets aren’t just technical resources — they’re financial commitments. Understanding depreciation and cost tracking isn’t about accounting paperwork; it’s about knowing when an asset stops being worth what your company is paying for it.
A proper IT asset management audit ensures that business costs are optimized and unnecessary expenses are eliminated.
Where to Focus Your Cost Tracking & Depreciation
Cloud Cost Visibility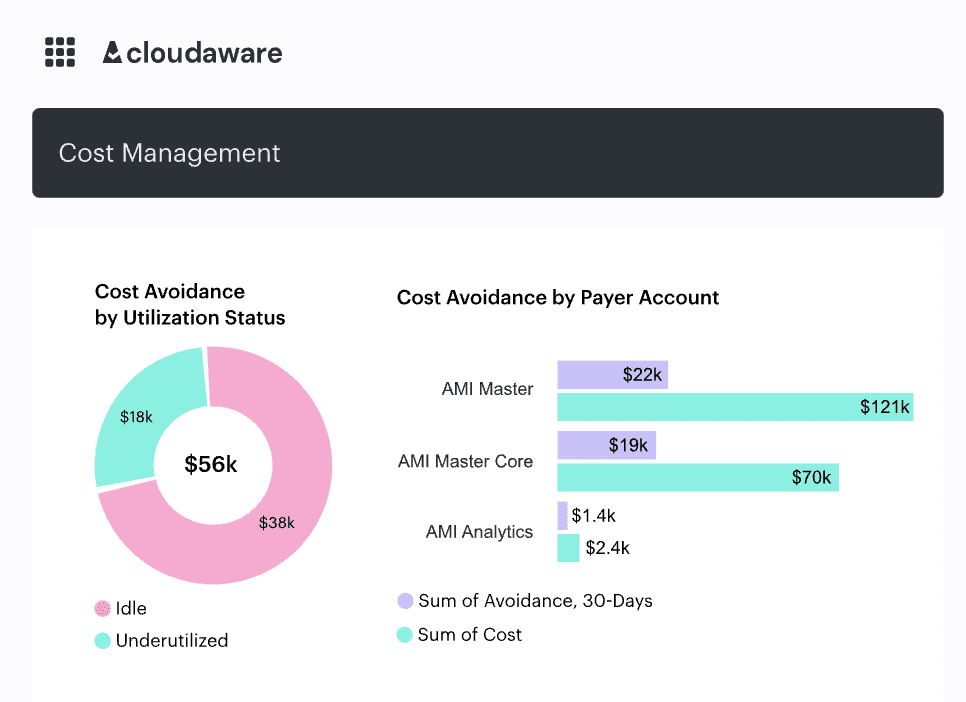
👉Every EC2 instance, Azure VM, GCP Compute Engine has a cost — even the ones that were forgotten months ago. Tracking daily, monthly, and annual spending trends ensures assets aren’t silently draining budgets.
👉Identify underutilized instances, overprovisioned resources, and unused storage volumes that should be right-sized or decommissioned.
👉Use asset management tools to allocate costs properly — linking resources to specific departments, cost centers, or projects prevents waste.
On-Premises Depreciation & Hardware Costs
👉 Track physical servers, storage arrays, and network equipment from acquisition to decommissioning — because once an asset is past its financial lifespan, it becomes a maintenance burden.
👉Assign depreciation schedules based on purchase date, warranty expiration, and projected replacement cycles — if a bare-metal server is still running five years past its cycle, it’s time for a replacement plan.
Cloudaware tracks cost allocation, flags underutilized compute resources, and provides lifecycle data to support business cost optimization.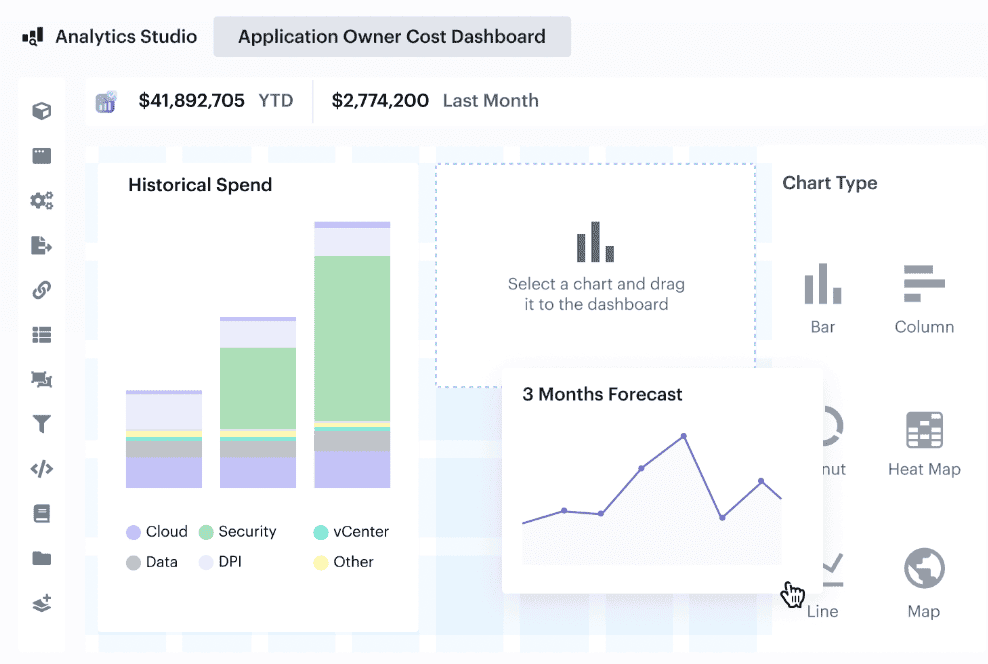
Cost tracking isn’t just about paying less — it’s about spending smart. Without real-time data, process visibility, and proper asset management software solutions, IT budgets bleed money without anyone noticing.
Automate your audits with Cloudaware
Managing an IT asset audit across a hybrid multi-cloud environment can feel like an endless cycle of chasing data, tracking compliance gaps, and generating reports — until you automate it with Cloudaware.
Instead of drowning in manual processes, Cloudaware helps your company stay ahead of audits, enforce policies, and generate audit-ready documentation — without the headache.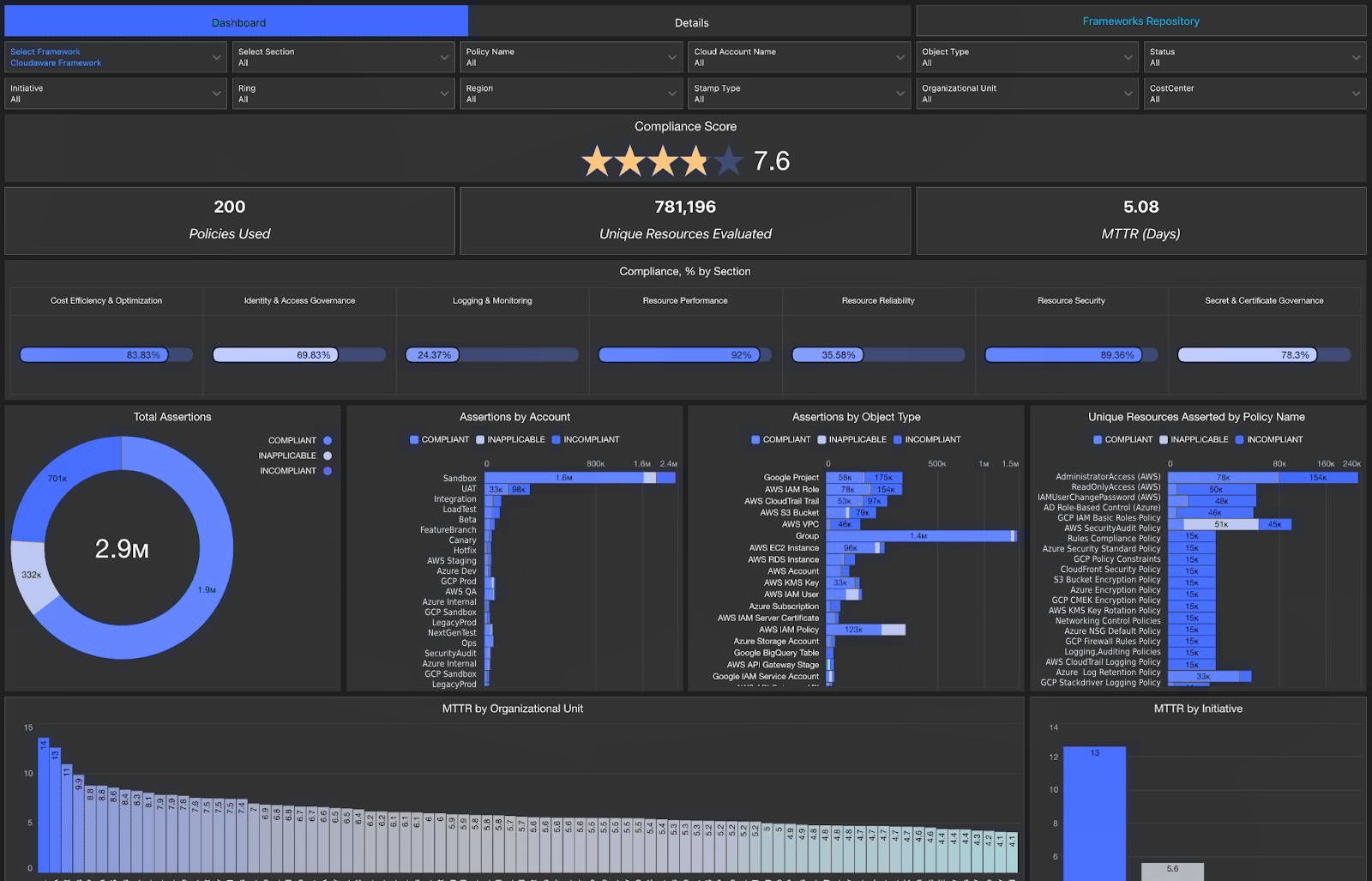
Cloudaware automatically compiles audit reports, consolidating insights from cloud, on-prem, and hybrid environments into one centralized, real-time dashboard — so your business is always prepared for an IT asset management audit report.
✅ Trigger notifications for upcoming audits, compliance checks, and expiring licenses, so nothing falls through the cracks.
✅ Generate audit reports instantly, with complete visibility into asset status, cost tracking, security posture, and lifecycle management.
✅ Ensure historical tracking of all IT assets — who created them, how they’ve changed, and whether they still meet compliance requirements.
✅ Work with a Cloudaware TAM expert to build custom reports tailored to your organization’s software asset management audit program, compliance frameworks, and IT asset management needs.
✅ Detect non-compliant assets (e.g., unpatched VMs, open ports, or missing encryption).
✅ Automatically generate remediation tickets in ServiceNow, Jira, or other ITSM tools, ensuring nothing is left unresolved.
✅ Schedule recurring compliance checks, enforcing security baselines across all environments.
Eliminate manual audits. Stay compliant, reduce risk, and automate the heavy lifting with Cloudaware’s asset audit software.
Read also
9 Configuration Management Best Practices for Multi-Cloud Setups
Top 8 CMDB Benefits: Why Companies Use Multi-cloud CMDB in 2025
Dependency mapping between CIs: 5-steps strategy to map infrastructure
What is service mapping: How It Works. Best Practices for IT Teams
