Every cloud instance in its place. Every CI mapped like a well-drawn constellation. No surprise bills creeping in. No security gaps lurking in the shadows. That’s what a rock-solid asset management process feels like — it just works.
In 2025, IT isn’t just fast; it’s a living, breathing ecosystem. Cloud assets spin up and down in seconds, configurations shift, costs fluctuate, and if you’re not ahead of it, you’re already behind.
The best teams?
They have a process — a six-step framework that keeps their multi-cloud environment clean, compliant, and cost-efficient.
At Cloudaware, we’ve seen it all. The wins, the facepalm moments, and the sneaky pitfalls that drain budgets overnight. So today, I’m laying it out: the six must-have steps for IT asset management success — plus the secret insights that help DevOps teams and cloud architects dodge the most common traps.
What is an IT asset management workflow
IT asset management (ITAM) is the structured process of tracking, managing, and optimizing all IT assets — hardware, software, cloud resources — throughout their lifecycle. It’s what keeps chaos at bay when thousands of cloud assets — EC2 instances, Kubernetes clusters, and software licenses — spin up and down daily.
Done right, the IT asset management process workflow ensures full visibility, airtight compliance, and zero budget surprises.
Done wrong… well, that’s when shadow IT, runaway costs, and security gaps creep in.
Now, let’s dive into the details of its workflow 👇
How does an IT Asset Management Process Work?
IT asset management is the rhythm that keeps your cloud infrastructure alive. Every EC2 instance, Kubernetes pod, software license, and piece of hardware has a pulse, moving through a lifecycle that needs to be tracked, optimized, and secured.
When the IT asset management workflow is tight, your company's multi-cloud environment runs like a well-oiled machine.
When it’s not? That’s when things slip through the cracks, budgets spiral, and security gaps emerge.
So, how does an IT asset management process actually work in a cloud-first world?
Here is a classic IT asset management process flow chart:
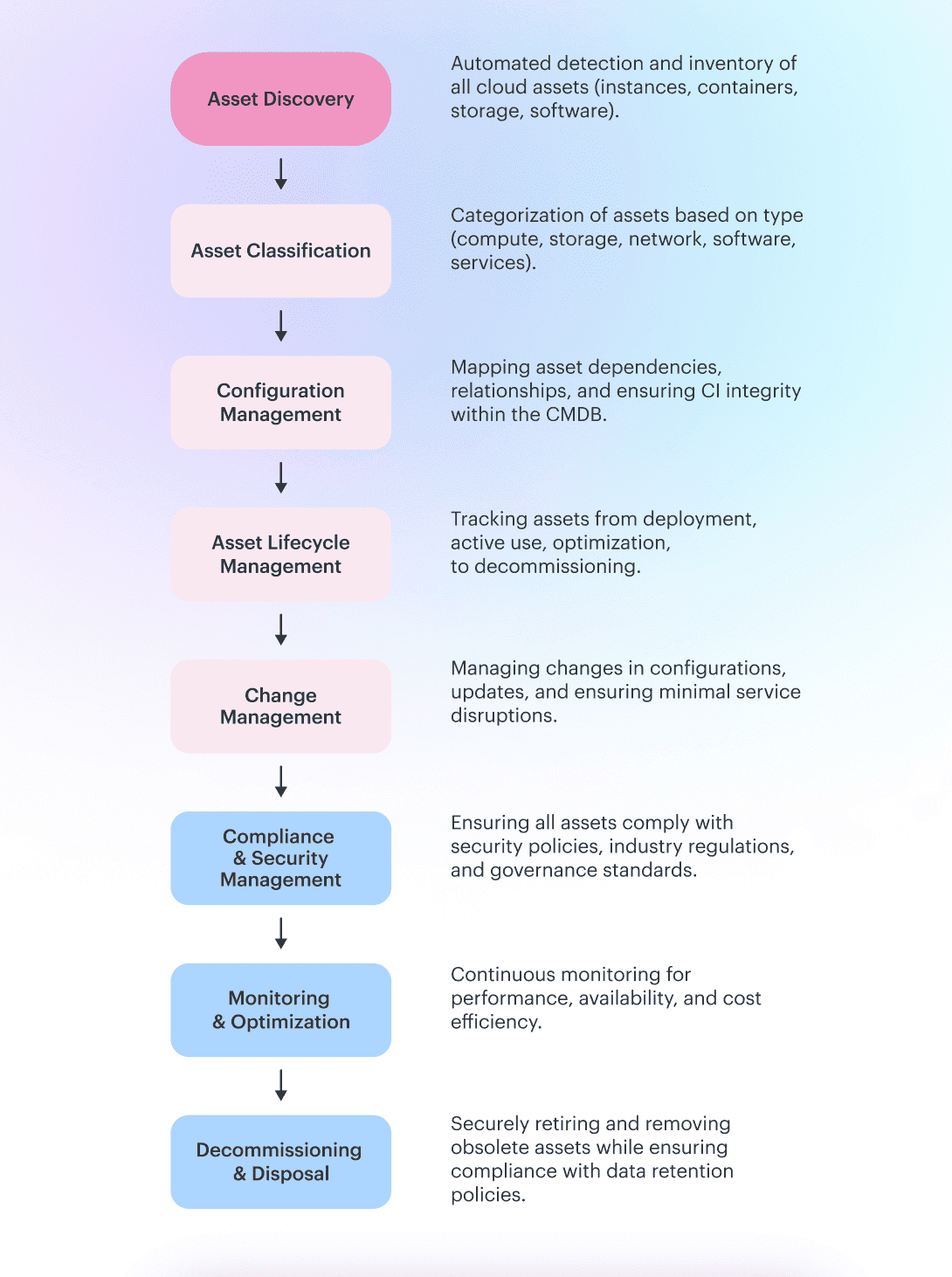
1. Asset Discovery: Seeing the Whole Picture
It starts with continuous asset discovery — a real-time scan across AWS, Azure, and GCP. Every compute asset (EC2, Azure VM, GCP Compute Engine), storage bucket (S3, Azure Blob, Google Cloud Storage), network resource (VPC, firewalls, security groups), and software license is detected, tagged, and cataloged. No blind spots in your IT asset management process.
2. Asset Classification
Next, assets are grouped into compute (VMs, Kubernetes nodes, Lambda functions), storage (databases, object storage, block storage), network (subnets, firewalls, security groups), software (SaaS tools, containerized apps, API gateways), and hardware (on-prem servers, network appliances, workstations). Each asset is assigned metadata — cost center, business unit, environment (prod/dev/test), and responsible owner — ensuring proper management.
Read also: How to conduct cloud cost analysis
3. Configuration Management: Connecting the Dots
The Configuration Management Database maps dependencies between assets. For example, a PostgreSQL RDS instance in AWS is linked to a business-critical application running in a Kubernetes cluster. A CloudFront CDN is tied to an S3 bucket storing customer data. Every dependency is logged, ensuring transparency in the IT asset management workflow.
4. Lifecycle Management: Keeping Cloud Clean
No more forgotten assets. Every resource follows a structured lifecycle: provisioned, actively used, optimized, decommissioned. If an EC2 instance runs at 10% CPU utilization for 30 days, it’s flagged for rightsizing. If a deprecated Kubernetes pod is still active, it gets reviewed. The IT asset management process ensures hardware and software assets don’t linger past their usefulness.
Read also: What is service mapping: How It Works. Best Practices for IT Teams
5. Change Management: Tracking Every Move
Every update, patch, and reconfiguration is logged. If a Terraform script deploys a new database, it’s recorded. If an IAM role changes permissions, it’s noted. This prevents security risks and ensures rollback options if something breaks.
6. Compliance & Security: Guardrails in Place
Assets are continuously checked against CIS Benchmarks, NIST standards, and internal security policies. If an S3 bucket is accidentally made public, it’s flagged. If a VM is missing encryption, alerts fire before it turns into a compliance issue. IT asset management isn’t just about tracking — it ensures governance and security across all assets.
7. Monitoring & Optimization: Running Lean, Running Smart
Live telemetry monitors performance, availability, and cost efficiency. If an underused EC2 instance, idle database, or misconfigured load balancer is wasting money, alerts are triggered. This management process ensures assets are running at peak efficiency without unnecessary costs.
8. Decommissioning: A Proper Goodbye
When an asset reaches the end of its lifecycle, it’s securely decommissioned, data is wiped, IAM roles are revoked, and compliance records are updated. No forgotten SSH keys. No lingering access. No unnecessary costs.
That’s IT asset management in action — a structured, automated, and security-first approach that turns cloud complexity into clarity. Keep the IT asset management process flowing, and your company's infrastructure stays ahead of the chaos 🚀
Read also: 10 Cloud Cost Optimization Tools That Actually Reduce the Bill in 2026
Asset management workflow example
Let’s talk about how Coca-Cola runs their asset management process — because managing a global operation means tracking a cloud fleet across AWS, Azure, and GCP without missing a beat.
-
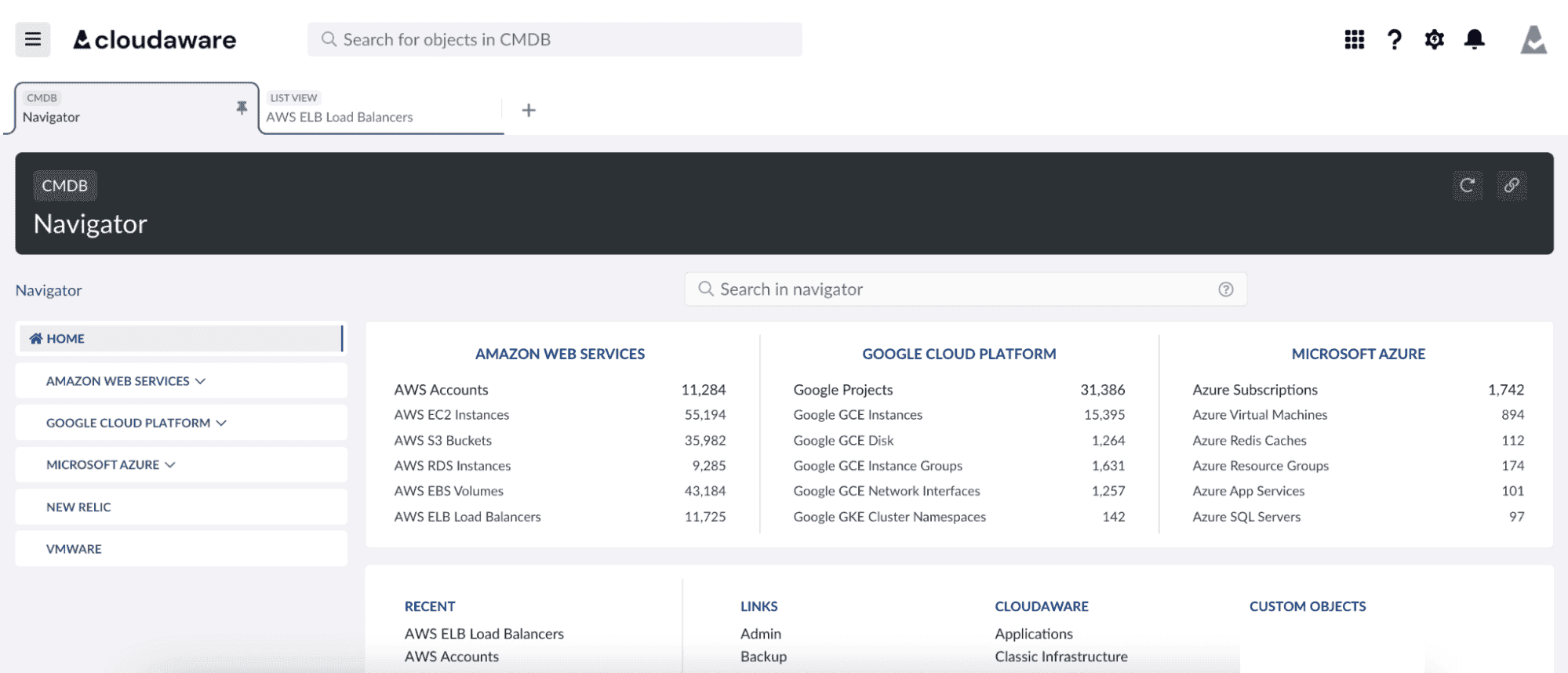
It all starts with asset discovery — a continuous heartbeat across the entire infrastructure. Every compute instance, storage bucket, and software license gets detected, classified, and tagged. Nothing goes unnoticed, and every asset is tied to a responsible owner.
-
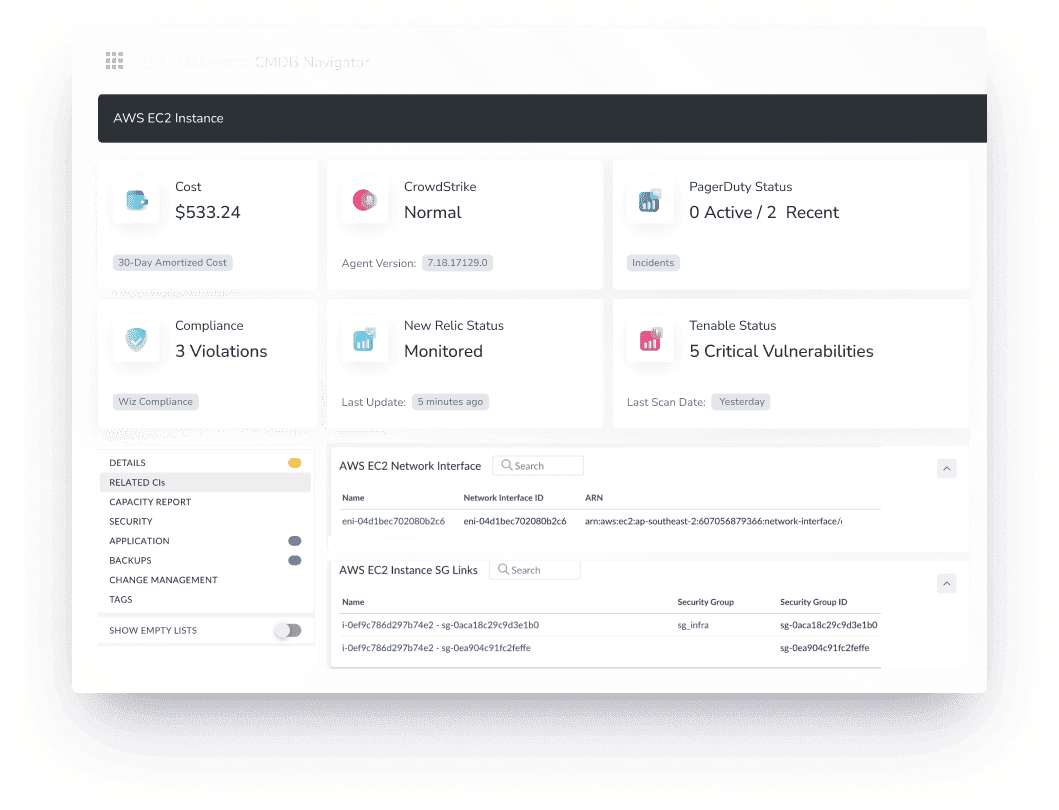
Then comes relationship mapping, where every IT asset finds its place in the ecosystem. This connects assets to applications, dependencies, and cost centers, making sure nothing is floating around unused, untracked, or out of policy.
-
Lifecycle management is the real game-changer. Every asset moves through deployment, active use, optimization, and decommissioning. If something is sitting idle or reaching end-of-life, it’s flagged before it turns into an expensive problem.
-
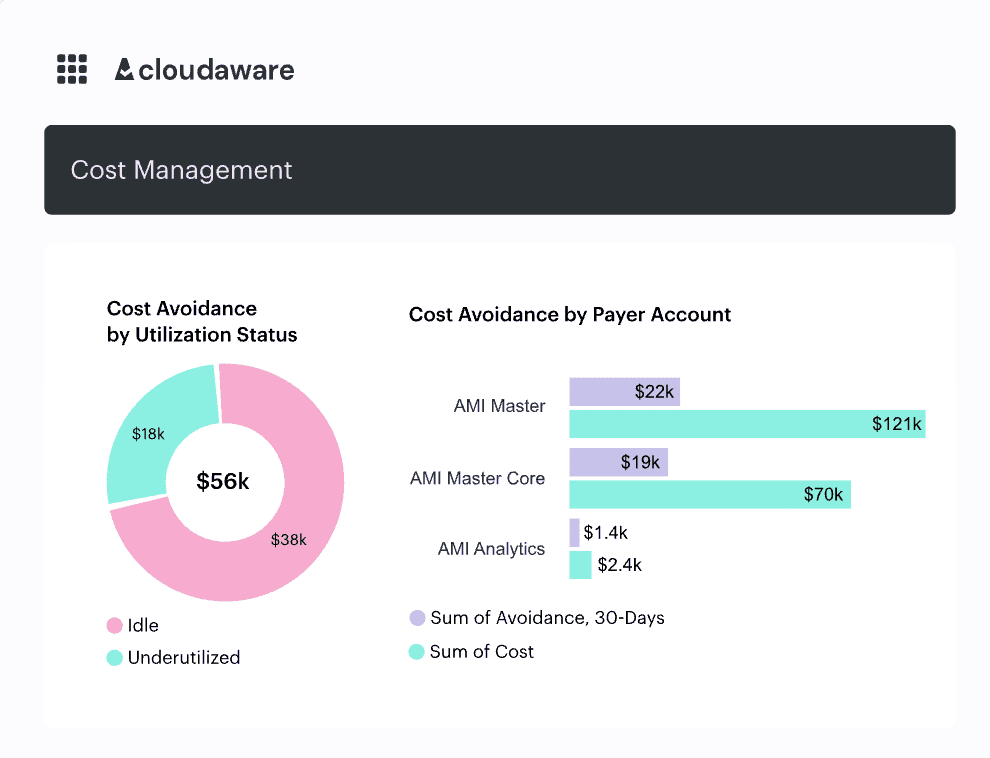
Cost tracking is on autopilot. Budgets don’t get blindsided because asset management is tied directly to spend, broken down by team, project, and service. If an unexpected spike happens, the system catches it before finance does.
-
And finally, compliance locks everything in place. Every asset is continuously checked against security policies, CIS benchmarks, and internal governance rules. If something drifts? It’s fixed before it turns into a risk.
That’s IT asset management in action — tight, efficient, and built to handle whatever the cloud throws at you.
Why it is important to keep IT smooth
Keeping your ITAM process running smoothly is like ensuring the engine of your multi-cloud infrastructure purrs without a hitch. When every component — hardware, software, and cloud assets — is accounted for and optimized, your company reaps significant benefits.
Here are the best advantage of a well-structured IT asset management process flow:
- When IT teams implement structured IT asset management, they reduce unnecessary spending and optimize resources. Organizations have reported up to 30% savings per asset in the first year of implementing ITAM practices.
Additionally, 11% of companies saved over $25 million, while 39% saved between $1 million and $10 million through software and hardware asset optimization. - A streamlined IT asset management process flow ensures every hardware and software asset is aligned with security policies to prevent costly breaches and compliance risks.
Without proper asset management, shadow IT, unpatched systems, and expired software licenses create vulnerabilities. In 2023, the average global cost of a data breach reached $4.45 million. - Tracking every asset across its lifecycle prevents over-provisioning, unnecessary spending, and unexpected failures.
- Understanding the full lifecycle of IT assets allows companies to plan upgrades, retire old resources, and align IT investments with business goals.
Read also: Top 8 CMDB Benefits: Why Companies Use Multi-cloud CMDB in 2025
A seamless IT asset management process isn’t just an IT best practice — it’s a business strategy. Keeping it smooth ensures cost control, security, and efficiency, making your company resilient in the ever-evolving cloud landscape.
But you’ll achieve this only if every aspect of your ITAM works ideally. Below you can find the secret collection of Cloudaware team insights 👇
Top 7 insights for IT asset management processes
1. Maintain an accurate and up-to-date IT asset inventory
One of our clients — a global company running a multi-cloud stack across AWS, Azure, and GCP — learned the hard way why IT asset inventory accuracy isn’t optional. Their CMDB had outdated Configuration Items, missing dependencies, and orphaned assets.
The result? Security gaps, unexpected costs, and compliance failures.
Here’s what fixed it: Automated asset discovery and continuous updates. Cloudaware integrated with their cloud accounts, pulling real-time CI data — from EC2 instances, Kubernetes clusters, and RDS databases to IAM roles and firewall policies. Each asset was enriched with cost data, security compliance status, and ownership details.
Then came automated lifecycle tracking. Unused VMs were flagged, outdated OS versions got alerts, and auto-remediation kicked in for policy violations.
An accurate IT asset inventory isn’t just about knowing what you have — it’s about controlling it before it controls you. Visibility is power.
2. Automate IT Asset Discovery and Monitoring
A client running AWS, Azure, and GCP had a problem. Their IT asset management processes were scattered — manual discovery left them with outdated CIs, missing dependencies, and security risks. EC2 instances ran unchecked, Kubernetes pods lingered long past their use, and firewall rules were misconfigured.
We set up automated IT asset discovery and real-time monitoring with Cloudaware. No agents, no gaps — just direct API integrations pulling fresh data. Within hours, they had full visibility into VM instances, security groups, IAM roles, and storage volumes.
Misconfigured firewall rules? Flagged. Unused compute resources? Identified. Compliance violations? Caught before they became audit failures. With automated alerts and enforcement, DevOps teams stopped firefighting and started optimizing.
Now, their IT asset monitoring runs itself. No more hunting down security gaps or untagged assets. Just control, clarity, and confidence that nothing is slipping through the cracks.
Read also: Dependency mapping between CIs: 5-steps strategy to map infrastructure
3. Standardize IT Asset Management Processes
Fixing IT asset discovery was just the start. The real challenge? Getting everyone on the same page. One of our clients — running AWS, Azure, and GCP — had teams deploying EC2 instances, RDS databases, and Kubernetes clusters however they wanted. No consistency. No governance. Just a sprawling mess of untagged, untracked, and over-provisioned assets.
So, we built standardized IT asset management processes into Cloudaware. Every new asset — whether a VM, storage volume, or security group — followed a defined workflow. Naming conventions? Enforced. Approval workflows? Required. Lifecycle rules? Built-in. No more orphaned resources draining costs or IAM roles lingering long past their purpose.
Now? They’re not just tracking assets — they’re controlling them. Every deployment is predictable, every decommissioning step is automated, and nothing falls through the cracks. Standardization isn’t about red tape — it’s about making IT operations clean, scalable, and secure.
Once it’s in place? Everything just runs smoother.
4. Implement a Lifecycle Management Approach
Getting IT asset management under control is one thing. Keeping it that way? That’s where lifecycle management comes in. Because without it, assets don’t just sit idle — they become security gaps, budget drains, and operational risks waiting to happen.
Picture a company running AWS, Azure, and GCP. Every day, new EC2 instances, Kubernetes clusters, and RDS databases are deployed. But no one’s asking: Who still needs them? Are they up-to-date? Should they even exist? Over time, forgotten IAM roles stay active, outdated software lingers, and orphaned resources keep stacking up.
With lifecycle management baked into Cloudaware, every CI follows a structured path. Provisioning requires approvals, aging assets trigger renewal or decommissioning workflows, and compliance checks catch unpatched systems before they become risks.
Now, nothing is left unchecked. Every asset has a purpose, an owner, and an expiration date. IT stays lean, security stays tight, and costs stay under control — exactly how it should be.
Read also: IT Asset Disposition - How to Close the Loop on Retired Assets
5. Leverage IT Asset Management (ITAM) Software
Running AWS, Azure, GCP, and on-prem infrastructure without IT asset management software is a recipe for inefficiency, risk, and uncontrolled spending. Assets don’t just exist — they move, scale, expire, and sometimes, get completely forgotten.
Here’s how ITAM software keeps everything in check:
✅ Real-time Asset Discovery. Detects every EC2 instance, Kubernetes cluster, RDS database, and VMware VM — no blind spots.
✅ Cost & Resource Optimization. Flags orphaned volumes, oversized VMs, and unused software licenses before they drain budgets.
✅ Security & Compliance Enforcement. Automates scans for misconfigurations, keeps CIS, NIST, and GDPR policies enforced, and prevents unauthorized IAM role sprawl.
✅ Lifecycle Management. Ensures assets are provisioned, maintained, and decommissioned at the right time — before they become risks.
ITAM software isn’t just about keeping a list — it’s about controlling what exists, optimizing what’s needed, and eliminating what isn’t.
Read also:
- What is the best Asset Management System for 2025: Top 3 Software
- Expert Review of Top 10 It Inventory Management Software For 2025
6. Regularly Review and Update
IT environments don’t break overnight. It happens slowly — a forgotten IAM role here, an oversized EC2 instance there, an unpatched RDS database no one touches anymore. One day, everything seems fine.
The next? You’re bleeding money, drowning in compliance gaps, and chasing security risks you didn’t see coming.
That’s why regular IT asset reviews aren’t just a process — they’re a discipline. A team I worked with manages thousands of CIs — VMs, databases, Kubernetes clusters, and security groups across AWS, Azure, and GCP. Now, every quarter, they audit unused resources, untagged assets, and outdated software in Cloudaware.
Every review catches something — a forgotten staging environment burning cash, a security rule too open, a CI misaligned with policy. No surprises. No runaway costs. Just a system that stays sharp, efficient, and secure — because it’s built to evolve.
7. Train Your Staff
You can automate asset tracking, lifecycle management, and compliance enforcement, but if your team isn’t trained to use the system right, gaps will form fast.
Start with role-based training:
📌 Cloud architects should master CI relationships, tagging strategies, and cost monitoring.
📌 DevOps teams need hands-on sessions in automated provisioning, security policies, and remediation workflows.
📌 Security teams should run compliance audits, detect misconfigurations, and enforce access controls.
Make it real — set up monthly live fire drills where teams respond to simulated incidents, decommission stale resources, and optimize deployments. A trained team doesn’t just manage assets. They master them.
Read also: 9 Configuration Management Best Practices for Multi-Cloud Setups
Achieve 100% control over your IT Assets with Cloudaware technology
Cloudaware isn’t just a CMDB — it’s the backbone of the ITIL asset management process, giving IT teams full control over their assets across AWS, Azure, GCP, and on-prem environments. Companies use it to streamline IT asset management, ensuring every resource is tracked, secured, and optimized.
At its core, Cloudaware delivers real-time inventory management and automated discovery. Every EC2 instance, Kubernetes cluster, firewall rule, IAM role, and RDS database is continuously scanned, logged, and mapped to its dependencies.
But raw data isn’t enough
-
Cloudaware enriches CIs with cost breakdowns, security posture, software details, and performance insights.
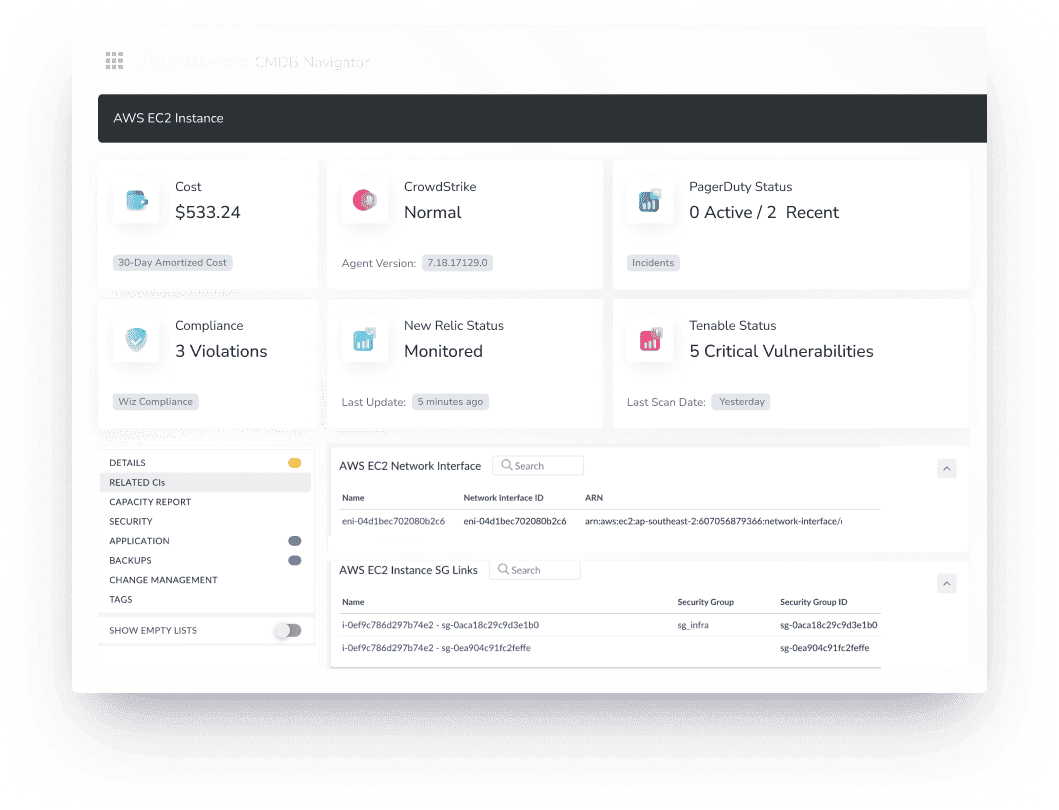
-
Then comes change tracking. Every modification — whether a misconfigured IAM role, an unapproved software install, or an unplanned deployment — is logged with full context, giving teams real-time visibility into asset changes.
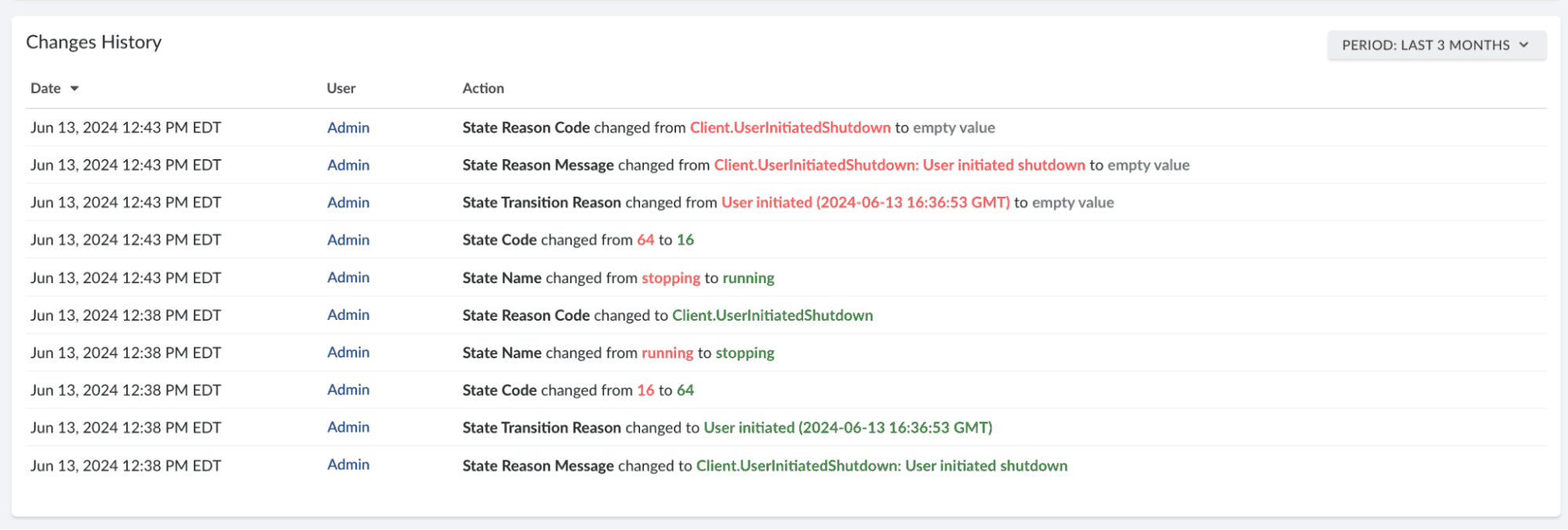
-
With automated workflows, Cloudaware enforces provisioning approvals, lifecycle tracking, and remediation policies, ensuring compliance and cost efficiency.
Cloudaware isn’t just another asset management system. It’s the difference between managing chaos and mastering IT operations.
